Manuscript accepted on :10-04-2023
Published online on: 03-06-2024
Plagiarism Check: Yes
Reviewed by: Dr. Rishit Jangde
Second Review by: Dr. Cherry Bansal
Final Approval by: Dr. Anton R Keslav
Department of Cell Biology and Molecular Genetics, Sri Devaraj Urs Academy of Higher Education and Research, Kolar, Karnataka, India.
Corresponding Author E-mail: kiranmayee@sduaher.ac.in
DOI : https://dx.doi.org/10.13005/bpj/2916
Abstract
Molecular docking is an important tool for connecting molecular biological structure to computer-aided drug design. The purpose of this blind docking experiment is to compare the binding energies of these three drugs and to predict the most likely binding poses of a ligand with a known three dimensional structure of a protein. To substantiate our previous in vitro study findings, an in silico model was chosen to compare the binding properties of the three drugs. The work is entirely bioinformatics in nature. Blind docking was accomplished with the help of free software/(s). A comparison was made among the three drgus, used primarily in cancer treatment, namely, anastrazole, capecitabine and quercetin. In our in vitro study, these three drugs were extremely effective. CB dock-2 to blind dock, SwissTargetPrediction to choose the targets, PubChem and Protein Data Base to obtain 3D structures of ligand and target respectively were used. Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, and Excretion (ADME) from SwissADME, drug likeness from MolSoft L.L.C. software, and Liponski’s rule was used to check the “Rule of five (RO5)”. The crystallographic structures have resolution values ranging from 1 Å to 3 Å. Lipinski’s rule of five, Swiss ADME and drug likeness were used to compare the three drugs. For all of the targets studied, quecetin appeared to have the highest AutoDock vina scores. To summarize the current findings and publicly available data, quercetin is chemoprotective and radioprotective to healthy/ normal cells and it can be used during cancer treatment.
Keywords
Anastrozole; Blind docking; breast cancer; Capecitabine; CB dock 2; protein data bank; Pubchem; Querecetin
Download this article as:| Copy the following to cite this article: Kiranmayee P. The Binding Capacity of the Lead Phytochemical Molecule to Cancer Cell Target Proteins and its Potential Anticancer Properties with Respect to Standard Drugs. Biomed Pharmacol J 2024;17(2). |
| Copy the following to cite this URL: Kiranmayee P. The Binding Capacity of the Lead Phytochemical Molecule to Cancer Cell Target Proteins and its Potential Anticancer Properties with Respect to Standard Drugs. Biomed Pharmacol J 2024;17(2). |
Introduction
The most commonly discussed cancer is breast cancer (BC). The current treatment has a short-term effect of slowing tumor development. Patients frequently experience relapses the disease1. Cell proliferation and apoptotic pathways fail during this process and cancer takes over. BC is slowed by eating nutritious foods and staying physically fit. Foods high in saturated fat, processed meat and so on raise circulating levels of endogenous estrogens, pro-inflammatory cytokines, and growth factors. These in turn contribute to the development of breast cancer2. Natural fruits and vegetables are high in antioxidants and thus protect against the development of BC. Regular consumption of fresh fruits and vegetable, triglycerides, soy products and limited consumption of red wine and carbohydrates raises polyphenol and fibre levels and provides tumorigenesis resistance3.
In silico/docking approach has been shown to improve the drug discovery process by using free online software (s) in less time as well as understanding and estimating the toxicity and efficiency of the small molecules or drugs4. The two of the qualities directly linked to the primary structure are selectivity and affinity. Protein (target) and ligand (drug) interaction will have to overcome difficulties such as toxicity because of non-specific protein binding and insufficient efficacy because of low affinity5.
Quercetin: The human diet is high in flavonoids which have promising therapeutic properties for a variety of illnesses, including cancer. The flavonoid quercetin has been extensively researched and is found in major amounts in commonly used plants such as Allium cepa, Brassica, Allium sativum, spinach and others. According to research, quercetin works well on malaria, inflammations, Alzheimer’s, obesity, and breast cancer on par with standard drugs6. Based on research findings, quercetin inhibits BC by preventing signal transduction, encouraging cancer cell apoptosis and suppressing cancer cell proliferation and metastasis7.
Anastrozole: Aromatase inhibitors of type II are non-steroids and anastrozole is a type II potent aromatase inhibitor. Anastrozole binds to the heme ion of aromatase in a reversible manner, lowers the levels of estrone (E1), 17-beta-estradiol (E2) and estrone sulphate (E1S). Aromatase inhibitors are the endocrine therapy of choice for treating breast cancer, particularly in postmenopausal women. Anastrozole is the first-line treatment choice for metastatic situations and postmenopausal women with oestrogen receptor-positive BC8.
Capecitabine: Synonym Xeloda, is a fluoropyrimidine deoxynucleoside carbamate antimetabolic drug. In in-vivo conditions, thymidine phosphorylase (dThdPase) converts this drug to 5-fluorouracil (5-FU). It is far more effective as an adjuvant treatment in metastasis and in advanced BC, also referred to as a rescue drug. It can be effective when combined with other medications9.
The benefits of combination therapy include improved or maintained efficiency, dose and toxicity reduction; and a delay in the development of drug resistance. In our previous study10, we established that a very low dose of quercetin (16 g/ml) inhibited cell growth, while increasing cell death, arresting cell cycle, inducing mitochondrial depolarization, and expressing caspase in combination with anastrozole and capecitabine. The current study backs up these findings by docking various BC proteins with the three drugs and comparing their efficacy in binding to the targets. Anti-apoptotic proteins, hydrolases, isomerases, oxidoreductases, transcription factors, binding proteins, signaling proteins, and transferases are all included in this category.
Material and Methods
CB dock was used to dock the drugs (anastrozole, capecitabine, and quercetin) with the target proteins. Each target protein was docked separately on each of the three ligands. A total 117 proteins were docked. The selected target molecules majorly belong to oxidoreductases/oxidoreductase inhibitors, hydrolases/hydrolase inhibitors, isomerases, kinase/kinase inhibitors, transferase/transferase inhibitors, hormone, and cell cycle transcription factors, growth factor receptors, apoptosis regulators, and signaling proteins. Small molecules’ interaction with targets enables biological functions, interpretation, prediction and drug development process. Blind docking aids in determining the precise binding sides of proteins and predicts the bind poses of any given molecule.
SwissADME
In silico methods predict Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, and Excretion (ADME) parameters based on available molecular structure. The Swiss ADME web tool, which is simple to use, assisted in predicting the physicochemical functions, medicinal chemistry, water solubility, drug-likeness, lipophilicity, and pharmacokinetics. To obtain all these mentioned parameters, the smiles from PubChem for Anastrozole, capecitabine, and quercetin were copied and submitted on the SwissADME page. Following completion, the “BOILED-Egg” button was pressed to record the key parameters of gastrointestinal absorption and blood-brain barrier (BBB)11.
Drug likeness
Drug likeness provides a balance between molecule properties and structure, determines the likelihood of a small molecule becoming an oral drug, and identifies the similarities to known drugs. This tool provides molecular formula, number of (hydrogen) bond donors and acceptors (HBA and HBD), logP, logS, pKA value, molecular weight, BBB, and likeness score after entering the smiles. The higher the probability, the higher the score value of an active drug. The water partition coefficient predicts an oral drug’s water solubility. High potency at the biological target is a required quality in drug candidate potency. It summarizes the ligand and lipophilic efficiencies. The number of (hydrogen) bonds versus side chains (alkyl) of a molecule is used to calculate solubility factor. Slower absorption and action result from lower solubility. Too many hydrogen bonds result in low-fat solubility and a failure to penetrate the cell membrane and act inside the cell. The LogP value should be between 0.4 and 5.6, the molecular weight should be from 160 to 480/ mol, and the molar refractivity should be from 40 to 130 with 20 to 70 atoms. The drug molecules’ molecular properties and drug likeness were provided by MolSoft L.L.C. software12.
Lipinski’s rule
The “Rule of five (RO5)” or “Lipinski’s rule” determines whether a predicted molecule adheres to five rules: molecular weight (<500 g/mol), hydrophobicity (Log P <5), HBA (no. <10), HBD (no. <5), Polar Surface Area (PSA) (≤140 A˚) and rotatable bonds (< 10Rot B). It determines the chemical’s oral bioavailability as well as its chemical and physical properties. A molecule is predicted to be a drug should if it meets at least three of the five rules, and a non-oral drug if it violates more than two rules13.
SwissTargetPrediction (STP)
This tool predicts innate small protein molecule targets. Humans provide the default prediction. STP works by providing smile input or by drawing the 2D structure protein probe molecules from PubChem (both synchronise automatically)14, 15.
Ligand and protein selection
PubChem provided the 3 dimensional (3D) drug structures and isomeric smiles for anastrozole, capecitabine, and quercetin16-19 and the RCSB protein databank (RCSB PDB) provided the protein targets20.
Docking study
CB-Dock2 was used in this study to detect protein surface curvature (CurPocket) and guide molecular docking by Auto Dock Vina (1.1.2 version). CB-dock has many benefits over other docking methods21 available. The four steps involved in quick protein-ligand blind docking are data input and processing; cavity detection, visualization and data analysis. CB dock2 examines the ligand for hydrogens, adds hydrogens and partial charges, generates the initial 3D confirmation, adds missing side chain atoms, adds hydrogen atoms, examines the missing residues, and removes the co-crystallized water and hetero groups.
Results and Discussion
A library of targets has been collected from the literature search and structures were retrieved from RCSB. The blind docking method is a model that can be preferred for understanding the relation between drug and target at atom level. It describes the ability of a drug or small molecule to bind to a target protein. It is a two-step process that aids in predicting ligand confirmation, position, orientation (pose), and affinity assessment.
The current study focuses on drug molecule interactions with target proteins in BCs. in vitro compared the efficiency of purified quercetin from radish leaves and dill weed leaves with anastrozole and capecitabine. Our findings indicated that quercetin, in conjuction with anastrozole and capecitabine, could reduce the toxic burden at a low concentration (16 µg/ml)10.
Docking experiments were conducted to determine which of the three drugs (anastrozole, capecitabine and quercetin) had the highest binding efficiency (Table 1). The protein targets were classified and docked against the three drug molecules using SwissTarget predictions and published literature.
 |
Table 1: The 3 dimensional structure, molecular weight, formula and canonical smiles of the selected drug. |
Molecular weight <5 denotes the light weight of the molecules, that can pass through the target cell’s membrane. Lower MW favours oral absorption, and higher molecules choose an alternate route namely through the membranes. The table shows the molecular weight of the selected compounds according to Lipinski’s rule. The test compound’s bioavailability radar revealed an immediate consideration of drug-likeness (Table 2 and Fig. 1). XlogP (between -0.7 and +5.0), MW (between 150 and 500 g/mol), polarity (TPSA: between 20 and 130 Å; a little higher for quercetin), solubility (Logs: <6), flexibility (rotatable bonds: <9) are the six major properties considered22.
Table 2: Physicochemical properties of anastrozole, capecitabine and quercetin from SwissADME
|
Property |
Anastrozole |
Capecitabine |
Quercetin |
|
Molecular weight (g/mol) |
293.37 |
359.35 g/mol |
302.24 g/mol |
|
Fraction Csp3 |
0.41 |
0.67 |
0.00 |
|
Number of rotatable bonds |
4 |
8 |
1 |
|
Number of HBA |
4 |
8 |
7 |
|
Number of HBD |
0 |
3 |
5 |
|
TPSA |
78.29 Å |
122.91 Å |
131.36 Å |
|
XLogP3 (lipophilicity) |
2.03 |
0.56 |
1.54 |
|
Log S (ESOL) |
-3.04 |
-2.07 |
-3.16 |
|
GI absorption |
High |
High |
High |
|
BBB permeant |
Yes |
No |
No |
|
Lipinski |
0 violation |
0 violation |
0 violation |
|
Synthetic accessibility |
2.21 |
4.67 |
3.23 |
|
Lead-likeness |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
|
Bioavailability |
0.55 |
0.55 |
0.55 |
 |
Figure 1: The bioavailability radar from Swiss ADME is presented. A: Anastrozole, B: Capecitabine, C: Quercetin |
The “BOILED-Egg” graphical output predicts two important ADME parameters at the same time: passive gastrointestinal absorption and BBB15. While the area in the figure represents passive absorption by GI track (Capecitabine and Quercetin), the yolk region (Anastrozole) has higher probability of penetrating the brain (Fig. 2).
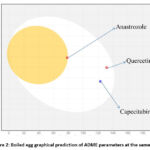 |
Figure 2: Boiled egg graphical prediction of ADME parameters at the same time |
The molecular properties of Ana, Cap, and Que were predicted using MolSoft. The outcomes are predicted in (Fig. 3). Green and blue lines represent non-drug and drug-like behavior. Non-drug peaks are those with values between zero and negative. Based on their drug-likeness scores, among the three, Capecitabine (positive value of 0.40) and Quercetin (positive value of 0.52) were considered drug molecules, whereas Anastrozole appears to be a non-drug (-0.95).
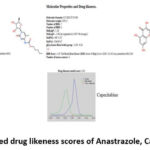 |
Figure 3: Plotted drug likeness scores of Anastrazole, Capecitabine and |
To modify the action of macromolecule targets, drugs or bioactive molecules shall bind to them. The mapping of targeted bioactive small molecules is an important step in understanding the molecular actions behind their activity and forecasting cross reactivity or potential side effects. The targeted classes for the three drugs tested were provided by SwissTargetPrediction (Fig. 4). The choice of a protein for docking research is critical, particularly its resolution. A crystal structure contains either protein or nucleic acid. The obtained data from these crystals is the measure of resolution. Majorly, the crystallographic structures have resolution values between 1 Å and 3 Å.
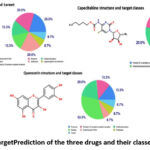 |
Figure 4: Swiss Target Prediction of the three drugs and their classes in percentages |
Apoptotic proteins as targets
A few anit-apoptotic proteins will be targeted to gain insight into the drug’s mode of action. With a few exceptions, anastrozole had higher vina scores than the other two with apoptotic proteins studied in the present work (Tables 3 and 4, Fig. 5).
Table 3: Apoptosis target classes used in the present study
|
Sl.No. |
Protein molecule |
RCSB id |
Length |
Resolution |
Vina score of the drugs used |
|
1. |
CASP8 and FADD-like apoptosis regulator |
3H13 |
272 |
2.20 Å |
A:-6; C:-6.8; Q:-6.9 |
|
2. |
Apoptosis regulator Bcl-X |
2YXJ |
181 |
2.20 Å |
A:-7.4; C:-6.9; Q:-7.2 |
|
3. |
Apoptosis regulator Bcl-2 |
2O2F |
138 |
A:-7.2; C:-6.9; Q:-7.1 |
|
|
4. |
Apoptosis regulator Bcl-2, Bcl-2-like protein 1 chimera |
4IEH |
169 |
2.10 Å |
A:-7.7; C:-6.8; Q:-7.2 |
|
5. |
Apoptosis inhibitor survivin |
1E31 |
142 |
2.71 Å |
A:-7.1; C:-7.5; Q:-7.5 |
|
6. |
Apoptosis regulator Bcl-2 |
2W3L |
144 |
2.10 Å |
A:-7.5; C:-7.7; Q:-7.4 |
|
7. |
Apoptosis regulator Bcl-X |
2YXJ |
181 |
2.20 Å |
A:-7.5; C:-6.9; Q:-7.1 |
|
8. |
Mcl-1 |
3KZ0 |
158 |
2.35 Å |
A:-7.1; C:-6.2; Q:-6.6 |
|
9. |
Bcl-2-like protein 1 |
3ZLN |
181 |
2.29 Å |
A:-9.1; C:-7.9; Q:-7.9 |
|
10. |
Induced myeloid leukemia cell differentiation protein Mcl-1 |
5IEZ |
159 |
2.60 Å |
A:-7.9; C:-7.7; Q:-8.5 |
|
11. |
Apoptosis regulator Bcl-2 |
1GJH |
166 |
|
A:-6.2; C:-6.2; Q:-6.9 |
Å: Angstrom; CASP: Caspase; FADD: Fas-associated death domain; Bcl-X: B-cell lymphoma extra; Bcl 2:B-cell lymphoma 2; Mcl-1: Induced myeloid leukemia cell differentiation protein
Table 4: Contact amino acids and varieties of bonds between the target and the ligand molecules belong to apoptotic proteins involved in breast cancer.
|
PDB |
Contact residues, bond pattern and number of bonds |
||
|
Anastrazole |
Capecitabine |
Quercetin |
|
|
3H13 |
SER318GLN3 Weak (2), hydrophobic (5) |
GLY317SER318 Weak (3), |
ASN262 TYR360SER411 Weak (3), Hydrogen (9), |
|
2YXJ |
THR344LYS345A Weak (1), hydrogen |
SER164 Weak (3), |
TYR120PHE123GLU Hydrogen (3), hydrophobic |
|
2O2F |
PHE101TYR105 Hydrophobic (9) |
PHE101ASP108 Hydrophobic (15), |
GLN96ALA97GLY Hydrophobic (7), |
|
4IEH
|
PHE63TYR67ASP70 Pi-pi (1), weak |
ALA59ASP62 TYR67LEU96ASN Pi-pi (1), weak (1), |
PHE63ASP70PHE VAL115 Pi-pi (1), weak (3), |
|
1E31
|
PHE13 LEU14LYS15 Hydrogen (3), |
PHE13LEU14LYS Hydrogen (7), |
PRO12PHE13L Hydrogen (7), |
|
2W3L |
LYS22ARG26SER Hydrogen (2), |
LYS22ARG26SER64 Hydrogen (7), |
LYS22ARG26 Hydrogen (7), |
|
3KZ0 |
GLN189ALA190 Hydrogen (5), |
GLN189ALA190 Hydrogen (3), |
ARG187THR191 Hydrogen (11), |
|
3ZLN |
PHE97ARG102 PHE146 Hydrogen (2), ionic (3), |
LYS16LYS20PHE97 Ionic (3), weak (4), |
LYS20PHE97 Ionic (2), cation |
|
5IEZ |
HIS224ALA227 Hydrogen (20, |
ASN239GLU240 Hydrogen (7), |
ASN239GLU240 Hydrophobic (3), |
|
1GJH |
HIS3ALA4GLY Hydrogen (2), cation pi (1), hydrophobic (7) |
HIS3ALA4GLY Pi-pi (1), hydrogen (6) hydrophobic (5) |
HIS3ALA4GLY5 Hydrogen (3), |
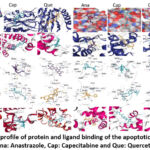 |
Figure 5: Docking profile of protein and ligand binding of the apoptotic proteins studied. Ana: Anastrazole, Cap: Capecitabine and Que: Quercetin |
Tumor cells escape, protect and develop drug resistance by avoiding receptor mediated apoptosis. C-FLIP (Cellular FLICE like inhibitory protein) is a key regulator protein in the extrinsic cell death pathway (FADD-like IL-1beta-converting enzyme inhibitory protein). Overexpression of c-FLIP protects the tumor cells. This is a capable caspase activation initiator and cell death inhibitor as well as an enhancer of procaspase-8 activation. Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL overexpression in cancer cells confers a survival benefit over standard chemotherapy (anti-apoptotic or pro-survival proteins). Survivin, a mitotic spindle fiber-associated protein, acts as an apoptosis activator. Myeloid cell Leukemia-1 is a Bcl-2 anti-apoptotic member. Anti-apoptotic protein over-expression promotes cell survival and proliferation. Targeting these proteins will aid in the development of new drugs and drug combinations20.
Hydrolases as targets
The vina scores of quercetin seem to be the highest among the three drugs tested by docking for hydrolases (Tables 5, 6) (Fig. 6)20. DPP-4 is a cell surface protein that either suppresses or activates tumors. MMP-9 is essential in inflammatory and oncological disorders. ADAMTSs are members of extracellular zinc metalloproteinase family. Chemokine receptors are cell migration receptors linked to cancer metastasis. VEGF is a type of angiogenesis factor. Chemokine receptors regulate cell migration, cancer, immune responses, inflammation, and so on. Butyrylcholinesterase (BChE) and its genes are found in a variety of human cancers. Tumorigenesis, cell proliferation, and cell differentiation have all linked to it. DHS36 interacts with RNA and DNA G-quadruples to control transcription and post-transcriptional regulation. Cysteine protease relates to the mammalian interleukin-1 beta converting enzyme (ICE). Caspases, the cysteine proteases, are key role players in apoptosis and inflammation. MMP-9 is a protein that is participates in inflammation, wound healing, tumour growth and metastasis20.
Table 5: Hydrolases target classes used in the present study.
|
Sl.No. |
Protein molecule |
RCSB id |
Length |
Resolution |
Vina score of the drugs used |
|
1. |
Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 soluble form |
4A5S |
740 |
1.62 Å |
A:-8;C:-7.2;Q:-9 |
|
2. |
Matrix metalloproteinase-9, |
5TH6 |
231 |
1.70 Å |
A:-7.3;C:-7.0;Q:-8.6 |
|
3. |
A disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs 4 |
4WKE |
235 |
1.62 Å |
A:-7.4;C:-7.5;Q:-8.6 |
|
4. |
C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4, Lysozyme Chimera |
3OE0 |
499 |
2.90 Å |
A:-7.9;C:-8.1;Q:-8.2 |
|
5. |
protein (vascular endothelial growth factor) |
1VPP |
102 |
1.90 Å |
A:-6.5;C:-6.6;Q:-6.7 |
|
6. |
NHE-RF1 |
4JL7 |
91 |
1.16 Å |
A:-6.7;C:-6.2;Q:-6.7 |
|
7. |
Apopain |
1PAU |
147 |
2.50 Å |
A:-5.8;C:-6;Q:-6 |
|
8. |
Caspase-8 |
1QTN |
164 |
1.20 Å |
A:-6.7;C:-7.2;Q:-7.2 |
|
9. |
Matrix metalloproteinase-9 (EC 3.4.24.35) (MMP-9) (92 kDa type IV collagenase) (92 kDa gelatinase) (Gelatinase B) (GELB) |
2OVX |
159 |
2.00 Å |
A:-8.1;C:-8.6;Q:-10.4 |
|
10. |
DEAH (Asp-Glu-Ala-His) box polypeptide 36 |
5VHE |
933 |
3.79 Å |
A:-8.5;C:-8.4;Q:-8.9 |
|
11. |
Cholinesterase |
4BDS |
529 |
2.10 Å |
A:-8.9;C:-8.2;Q:-9.3 |
|
12. |
C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4, Lysozyme Chimera |
3ODU |
502 |
2.50 Å |
A:-8.3;C:-7.9;Q:-8.3 |
|
13. |
C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4, Lysozyme Chimera |
3OE9 |
499 |
3.10 Å |
A:-8.2;C:-7.2;Q:-8.1 |
|
14. |
C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4, Lysozyme Chimera |
3OE8 |
502 |
3.10 Å |
A:-8.6;C:-7.6;Q:-8.2 |
|
15. |
C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4/Endolysin chimeric protein |
4RWS |
498 |
3.10 Å |
A:-7.5;C:-7.1;Q:-8.2 |
|
16. |
Beta-secretase 1 |
4IVT |
433 |
1.60 Å |
A:-7.4;C:-7.1;Q:-7.8 |
NHE-RF1: Sodium (+)/Hydrogen (+) exchange regulatory cofactor 1
Table 6: Contact amino acids and varieties of bonds between the target and the ligand molecules belong to hydrolases involved in breast cancer.
|
PDB |
Contact residues, bond pattern and number of bonds |
||
|
Anastrazole |
Capecitabine |
Quercetin |
|
|
4A5S |
PRO475GLY476 Ionic (2), hydrogen (5), |
GLN314MET325 Cation pi (1), ionic (2), |
PRO475GLY476MET Hydrophobic (11), weak (6) |
|
5TH6 |
ARG143LEU147LEU Cation pi (2), hydrophobic |
ARG143LEU147 Cation pi (2), |
LEU397VAL398 Hydrophobic (7), |
|
4WKE |
THR326ASP328THR Cation pi (3), |
GLY323ASP328 Hydrogen (9), |
ASP328THR329 hydrogen (8), (6), hydrophobic (4), |
|
3OE0 |
ALA137ILE138ALA Hydrogen (4), |
ARG30GLU32ASN33 Hydrogen (7), |
ALA137ILE138 Hydrogen (9), |
|
1VPP |
ASP34ILE35PHE Hydrogen (1), |
GLU64Chain Hydrogen (10), |
ILE35PHE36 Hydrogen (2), |
|
3OE8 |
LEU41TYR45PHE Hydrogen bond (1), |
HIS113TYR11 Weak hydrogen (2), |
TYR45PHE93 Hydrogen (6), hydrophobic (6), |
|
4JL7 |
LYS19ASN22GLY Weak hydrogen (1), |
ASN22GLY23TYR Weak hydrogen (2), |
LYS19GLY23TYR24 Weak hydrogen (3), |
|
3OE9 |
LEU41TYR45PHE93 Ionic (2), |
TRP94ASP97HIS113 Weak hydrogen (6), |
LEU41TYR45TRP94ASP97 Weak hydrogen (3), Hydrogen (9), |
|
4RWS |
HIS113TYR116 Weak hydrogen (2), |
ALA137ILE138ALA Weak hydrogen (2) |
HIS113TYR116 Weak hydrogen (2) |
|
3ODU |
LEU41TYR45PHE Weak hydrogen (1), |
GLU31GLU32ASN Ionic (1), hydrogen (3) |
GLU32LEU41TYR45 GLU288 Hydrogen (4), pi-pi (1) |
|
4BDS |
ASP70GLY78SER Ionic (3), pi-pi (1) hydrophobic(7), weak hydrogen (5), hydrogen (10) |
TRP82GLY115GLY Hydrophobic (14), |
GLN67ASN68ILE Ionic (1), |
|
5HVE |
LYS78GLU79GLU Ionic (3), hydrophobic (7), |
PHE579ASN584ILE MET894 Ionic (3), |
LEU343PRO637 LEU892 Ionic (1), cation-pi (1), |
|
1PAU |
THR177HIS237 Hydrogen (6), |
MET176THR177HIS Hydrogen (5), |
ChainA:GLU191THR Hydrogen (6), |
|
1QTN |
LYS253 LEU254 SER256ILE257 Ionic (1), cation pi (2), |
LYS320GLY321PRO Hydrogen (10), |
LYS253LEU254 Cation-pi (1), |
|
2OVX |
GLN126VAL167 Hydrogen (6), |
GLY186LEU187 426PRO430 Hydrophobic (8), hydrogen (3), weak hydrogen (2) |
LEU188LEU397VAL398 Hydrogen (8), weak hydrogen (3), hydrophobic (7) |
 |
Figure 6: Docking poses of hydrolases with the ligannds |
Isomerases as targets
The vina scores of quercetin were the highest of the three drugs tested (Tables 7, 8) (Fig. 7)20. Type IIA DNA topoisomerases are required for the maintenance of higher order DNA structure. The double standard DNA is covalently joined by human topoisomerase I. Type II topoisomerases (TOP2s) cleaves both the DNA duplex and cause cancer cell death. Kinase complexed mTOR is an important growth and proliferation regulator. DNA topoisomerases, particularly type IIA topoisomerases, have been identified as anti-bacterial and anti-cancer drug targets. Topoisomerase-targeting anticancer drugs work by poisoning topoisomerase, causing replication fork arrest and double-strand break formation20.
Table 7: Isomerases target classes used in the present study.
|
Sl. No. |
Protein molecule |
RCSB id |
Length |
Resolution |
Vina score of the drugs used |
|
1. |
Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase FKBP5 |
4DRH |
144 |
2.30 Å |
A:-8.4; C:-8.5;Q:-8.4 |
|
2. |
DNA topoisomerase 2-beta |
3QX3 |
803 |
2.16 Å |
A:-8.5;C:-7.8;Q:-9 |
|
3. |
DNA topoisomerase I |
1K4T |
592 |
2.10 Å |
A:-8.5;C:-8.4;Q:-9.1 |
|
4. |
DNA topoisomerase II, alpha isozyme |
1ZXM |
400 |
1.87 Å |
A:-8.9;C:-8.5;Q:-10.1 |
|
5. |
DNA topoisomerase I |
1T8I |
592 |
3.00 Å |
A:-8.3;C:-8.2;Q:-8.9 |
FKBP5: FK506-binding protein 5
Table 8: Contact amino acids and varieties of bonds between the target and the ligand molecules belong to isomerases involved in breast cancer.
|
PDB |
Contact residues and bond pattern |
||
|
Anastrazole |
Capecitabine |
Quercetin |
|
|
IZXM |
ASN91ALA92 Hydrogen (8), |
TYR34GLU87ASN 149ASN150THR159 Hydrogen (13), |
ASN91ALA92ASP94 Hydrogen (19), |
|
1K4T |
LYS354ILE355GLU Hydrogen (3), |
LYS202TRP203LYS ASP757 Hydrogen (27), |
ASN352LYS354ILE355 GLU356 PHE361LYS374 Hydrogen (24), |
|
3QX3 |
ARG503GLY776 Weak hydrogen (2), |
GLU477GLY Weak hydrogen (7), |
LYS456GLY478 Weak hydrogen (11), |
|
4DRH |
TYR57PHE67ASP Ionic (2), hydrogen |
TYR57ASP68SER Ionic (1), hydrogen (5), |
ASP68HIS71PHE Ionic (2), hydrogen (4), |
|
1T81 |
ASN352LYS354ILE Weak hydrogen (4), hydrogen (16), ionic (2), pi-pi (9), hydrophobic (8) |
ILE355GLU356PRO Weak hydrogen(6), hydrogen (21), ionic (2), pi-pi (11), hydrophoic (12) |
ASN352GLU356PR Weak hydrogen (6), |
 |
Figure 7: Interaction between the isomerase targets and ligands. |
Oxidoreductases as targets
The vina score of quercetin is the highest among the tested drugs against the goals of oxidoreductases (Tables 9, 10) (Fig. 8)20. Myeloperoxidase (MPO), a neutrophilic enzyme, promotes oxidative stress in a number of inflammatory pathologies. Catalysis of human cytochrome P450 aromatase enzyme results to form estrogens from androgens. Human Aldehyde dehydrogenase 1A3’s expression is more in cancers. COX takes charge of the increased production of prostaglandins during inflammation. P450 1A2 is accountable for the activation of carcinogenic compounds. Increased GSH levels in tumor cells are linked to tumor progression and resistance to chemotherapeutic drugs. Cancer cells show elevated levels of FTO expression. eNOS is involved in promotion or inhibition of cancer etiology. Cyclooxygenase 1 is an anti-inflammatory responsive enzyme. Aromatase inhibitors are thus first-line therapy for estrogen-dependent breast cancer.
Table 9: Oxidoreductases target classes used in the present study
|
Sl. No. |
Protein molecule |
RCSB id |
Length |
Resolution |
Vina score of the drugs used |
|
1. |
Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2 |
3LN1 |
587 |
2.40 Å |
A:-8.5;C:-8.3;Q:-9.8 |
|
2. |
prostaglandin h2 synthase-1 |
1EQH |
580 |
2.70 Å |
A:-8.0;C:-8.0;Q:-9.2 |
|
3. |
Corticosteroid 11-beta-dehydrogenase isozyme 1 |
2ILT |
275 |
2.30 Å |
A:-8.1;C:-8.6;Q:-8.8 |
|
4. |
Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2 |
5KIR |
551 |
2.70 Å |
A:-8.7;C:-8.4;Q:-9.5 |
|
5. |
myeloperoxidase light chain |
4C1M |
108 |
2.00 Å |
A:-8.1;C:-8.1;Q:-9.6 |
|
6. |
Cytochrome P450 19A1 |
3S7S |
503 |
3.21 Å |
A:-8.4;C:-7.6;Q:-8 |
|
7. |
Aldehyde dehydrogenase family 1 member A3 |
6TRY |
512 |
2.90 Å |
A:-8.3;C:-8.3;Q:-8.9 |
|
8. |
endothelial Nitric-oxide synthase |
1M9K |
415 |
2.01 Å |
A:-7.5;C:-7.8;Q:-9.5 |
|
9. |
Cytochrome P450 2C9 |
1R9O |
477 |
2.00 Å |
A:-8.3;C:-7.8;Q:-8.2 |
|
10. |
Inducible nitric oxide synthase |
4NOS |
427 |
2.25 Å |
A:-8.5;C:-7.6;Q:-9.3 |
|
11. |
Cyclooxygenase-2 |
4COX |
587 |
2.90 Å |
A:-8.4;C:-8.6;Q:-9.5 |
|
12. |
Cytochrome P450 1A1 |
6DWN |
491 |
3.00 Å |
A:-8.3;C:-8.6;Q:-10.5 |
|
13. |
Cytochrome P450 1A2 |
2HI4 |
495 |
1.95 Å |
A:-8.6;C:-9;Q:-9.8 |
|
14. |
Polyphenol oxidase |
2Y9X |
391 |
2.78 Å |
A:-8.2;C:-7.6;Q:-9 |
|
15. |
Glutathione reductase |
3DK8 |
478 |
1.10 Å |
A:-6.9:C:-7.9;Q:-8.9 |
|
16. |
Protein fto |
3LFM |
494 |
2.50 Å |
A:-7.8;C:-7;Q:-7.7 |
|
17. |
Prostaglandin G/H synthase 1 |
2OYE |
600 |
2.85 Å |
A:-8;C:-8.1;Q:-9.1 |
|
18. |
Cytochrome P450 19A1 |
3EQM |
503 |
2.90 Å |
A:-8.2;C:-7.7;Q:-8 |
|
19. |
Cytochrome P450 21-hydroxylase |
4Y8W |
482 |
2.64 Å |
A:-8;C:-7.9;Q:-8.7 |
|
20. |
Aldehyde dehydrogenase family 1 member A3 |
6TE5 |
512 |
3.25 Å |
A:-8.2;C:-8.3;Q:-8.9 |
|
21. |
Aldehyde dehydrogenase family 1 member A3 |
7A6Q |
512 |
2.95 Å |
A:-8.3;C:-8.1;Q:-9 |
|
22. |
Prostaglandin h2 synthase-1 |
1EQG |
580 |
2.61 Å |
A:-7.6;C:-8;Q:-9.2 |
|
23. |
Aldehyde dehydrogenase family 1 member A3 |
5FHZ |
529 |
2.90 Å |
A:-8.2;C:-8.4;Q:-9.1 |
Table 10: Contact amino acids and varieties of bonds between the target and the ligand molecules belong to oxidoreductases involved in breast cancer.
|
PDB |
Contact residues, bond pattern and number of bonds |
||
|
Anastrazole |
Capecitabine |
Quercetin |
|
|
1EQH |
PHE142SER143VAL145 Hydrogen (3), |
PHE142SER143VAL Hydrogen (7), |
ALA199ALA202 Hydrogen (7), |
|
2ILT |
THR40GLY41ALA Hydrogen (6), |
GLY41ALA42LYS Hydrogen(11), |
THR40GLY41AL ALA223 Hydrogen (12), |
|
3lN1 |
HIS75ARG106GLN Hydrophobic (8), |
ASN19CYS21CYS Hydrophobic (11), |
ASN19CYS21 Ionic (4), |
|
4C1M |
ALA28PHE29VAL Hydrophobic (8), |
MET87GLY90GLN91 Hydrophobic (7), |
PHE86MET87GL ARG239GLU242 Cation-pi (1), |
|
5KIR |
CYS36HIS39PRO40 CYS41 GLN42ASN43ARG ARG469 Hydrophobi (10), |
TRP323GLN327ASN Hydrophobic (9), |
ASN34CYS36HIS Hydrophobic (5), |
|
1EQG |
PHE142SER143 Hydrogen (4), |
PHE142SER143VAL Hydrogen (9), |
ALA199PHE200 Hydrogen (11), |
|
3S7S |
ARG115ILE132 141ARG145PHE GLY439 Cation pi (1), |
ARG115ILE132ILE Hydrophobic (18), |
ARG115ILE132IL Cation pi (1), |
|
1R9O |
ARG97ILE112 Pi-pi stacking (1) |
ARG97ILE112VAL ALA477 Hydrophobic (12), |
ARG97VAL113A Hydrophobic (8), |
|
6TE5 |
ARG276ASN485 Hydrogen (9), |
LYS266ARG276VAL Weak hydrogen (7), |
LYS266VAL277 Hydrophobic (6), |
|
2Y9X |
PHE97TYR101ALA Hydrophobic (8), |
GLN307THR308TYR Hydrophobic (8), |
SER2ASP3LYS5ASP Hydrophobic (2), |
|
6TRY |
PRO179TRP180ASN Hydrophobic (7), |
LYS266ARG276 Hydrophobic (8), |
HIS168ARG276L Pi-pi stacking (1), |
|
3EQM |
ARG115ILE132I Cation pi (1), hydrogen |
ARG115ILE132IL Hydrogen (15), |
ARG192GLN218 Pi-pi (2), cation pi (1), |
|
3lFM |
ILE85THR92PRO93 GLU234ARG322 Pi-pi stacking (2), |
ILE85THR92PRO93 Pi-pi stacking (2), |
ILE85ARG96TYR Cation-pi (1), |
|
4COX |
CYS36ASN39PRO Ionic (3), hydrophobic |
ASN34CYS36CYS37 Hydrophobic(6), |
ASN34CYS36CYS Hydrophobic (9), |
|
1M9K |
GLN90GLY92PRO Hydrophobic (8), |
TRP74TRP445PHE Hydrophobic (9), |
VAL71LYS72ASN Hydrophobic (11), |
|
2HI4 |
ARG108LEU123THR CYS458ILE459LEU497 Cation-pi (1), |
ARG108THR124PHE Hydrophobic (19), |
ARG108ILE117T Hydrophobic (18), |
|
4NOS |
TRP90TRP461PHE476 PRO467 Pi-pi stacking (1), |
LEU125ALA197 Pi-pi (2), cation pi(1), |
GLY117SER118 MET480 Pi-pi stacking (3), weak hydrogen (5), |
|
3DK8 |
CYS58CYS63VAL GLN445 Hydrophobic (1), |
GLY27GLY28GLY ALA342 Hydrophobic (5), |
GLY27GLY28 Hydrophobic (2), |
|
2OYE |
CYS36TYR39PRO40 ARG469 Ionic (1), |
ASN34CYS36TYR39 Ionic (1), weak hydrogen (5), hydrogen (7), Hydrophobic (7) |
ALA199PHE200A Weak hydrogen pi-pi (1), cation-pi (1) |
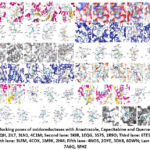 |
Figure 8: Docking poses of oxidoreductases with Anastrazole, Capecitabine and Quercetin ligands |
Proteins as targets
Table 11 provides the vina score comparison; wherein, quercetin showed the highest vina score for protein binding targets and table 12 shows the contact residues and bonds (Tables 11, 12) (Fig. 9)20. Overexpressed HSP90 aids transformation by stabilizing the mutated and overexpressed onco-proteins identifed in BC cells. Carcinoma-associated antigen is the epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM). HER 2, a member of an oncogenic protein family, involves in development and progression of breast cancers that are aggressive. Methenyltetrahydrofolate Synthetase regulates carbon flow by one-carbon metabolic network, which provides vital constituents for cell growth and proliferation; reserve has been shown to arrest the cell growth. ALDH1A3 is overexpressed and important for tumor cell’s vitality. HER 2 stimulates cell propagation in tissues. ER binds to either of structurally and functionally distinct ERs (ERα and ERβ). PKC delta’s C2 domain is activated by diacylglycerol, and functions as a tumor suppressor, a regulator of cell cycle progression (positive) and a regulator of apoptosis (positive or negative). Estrogen Receptor alpha LBD, (a novel isoform of ERα), promotes endocrine resistance and cancer proliferation (breast). Ephrin type-A receptor 2 (EphA2) (a receptor tyrosine kinase), overexpresses in breast cancers (human) and involves in a variety of serious progressions related to malignant breast progressions, including proliferation, migration, survival, invasion, metastasis, drug resistance, and angiogenesis20.
Table 11: Protein binding target classes used in the present study EphA2: ephrin type-A receptor 2
|
Sl. No. |
Protein Molecule |
RCSB id |
Length |
Resolution |
Vina score of the drugs used |
|
1. |
Estrogen receptor |
4PPS |
244 |
1.93 Å |
A:-7.2;C:-7.5;Q:-7.7 |
|
2. |
Estrogen receptor |
4PP6 |
244 |
2.20 Å |
A:-7.3;C:-7.2;Q:-8.4 |
|
3. |
Protein kinase C, delta type |
1YRK |
126 |
1.70 Å |
A:-6.3;C:-6.4;Q:-7.1 |
|
4. |
Estrogen receptor beta |
4J26 |
240 |
2.30 Å |
A:-6.9;C:-7.4;Q:7.7 |
|
5. |
estrogen receptor alpha (hER alpha) (protein (estrogen receptor alpha) |
3ERT |
261 |
1.90 Å |
A:-8.1;C:-7.5;Q:-7.8 |
|
6. |
EphA2 ectodomain |
2X10 |
545 |
3.00 Å |
A:-6.5;C:-5.8;Q:-6.5 |
|
7. |
Stress-70 protein, mitochondrial |
3N8E |
182 |
2.80 Å |
A:-7.4;C:-7.6;Q:-7.7 |
|
8. |
Aldehyde dehydrogenase family 1 member A3 |
6S6W |
489 |
3.25 Å |
A:-8.1;C: -8.5; Q:-9.0 |
|
9. |
5,10-Methenyltetrahydrofolate cyclo-ligase |
3HY3 |
203 |
1.80 Å |
A:-8.4; C:-7.4; Que:-8.2 |
|
10. |
Met and epithelial cell adhesion molecule |
6I07 |
262 |
2.35 Å |
A:-6.8; C:-6.9;Q:-7.2 |
Table 12: Contact amino acids and varieties of bonds between the target and the ligand molecules belong to binding proteins involved in breast cancer.
|
PDB |
Contact residues, bond pattern and number of bonds |
||
|
Anastrazole |
Capecitabine |
Quercetin |
|
|
6S6W |
PRO179TRP180 Ionic (2), pi-pi, (1) |
LYS266ARG276 Ionic (4), hydrogen |
LYS266LYS275 Ionic (4), hydrogen (14), |
|
4PPS |
MET343LEU346 Ionic (2), weak hydrogen |
GLU323PRO324PRO Hydrogen (2), |
MET343LEU346 Hydrophobic (13), |
|
4PP6 |
MET343LEU346 Hydrophobic (26), |
GLU323PRO324 Hydrophobic (16), |
MET343LEU346 Hydrogen (7), ionic |
|
1YRK |
MET32GLU34 ARG67GLN8 PHE12 Hydrogen (2), pi-pi (2) |
THR50MET51 Hydrogen (8), ionic (1), |
PHE4LYS48PRO49ASP60 Hydrogen (7), |
|
3ERT |
MET343LEU346 Hdrogen (3), |
LEU320GLU323 Hydrogen (4), |
MET343LEU346THR LEU525MET528 Hydrogen (5), ionic (1), |
|
2X10 |
GLN56 Hydrophobic (5), |
VAL364THR365CYS366 Weak hydrogen (3), |
THR365CYS366PRO HIS390 Hydrophobic (7), |
|
3N8E |
ILE447GLU448 ILE518VAL520 Hydrophobic (14), |
ILE447GLU448THR GLY587 Hydrophobic (14), |
ILE447GLU448THR Hydrophobic (13), |
|
3HY3 |
ILE54PHE55LEU Pi-pi (2), weak hydrogen (1), |
LEU56MET58PRO LYS150GLY151TYR152 Pi-pi (2), hydrogen (4), |
PHE55 LEU56 SER57 TYR152TYR153 Hydrogen (10), weak |
|
4J26 |
ARG466HIS467ASN Hydrogen (4), cation-pi |
GLU276PRO277 Hydrogen (2), cation-pi, |
MET295LEU298LEU Hydrogen (7), |
|
6I07 |
ARG125PRO257 Hydrophobic (4), hydrogen (3), weak hydrogen (2), pi-pi (1) |
GLU217LYS221 Hydrophobic, hydrogen |
ASP1ILE2VAL3MET4T Hydrophobic (3), hydrogen (9), weak hydrogen (4) |
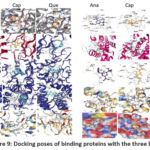 |
Figure 9: Docking poses of binding proteins with the three ligands |
Signal proteins as targets
With a minor difference, among the three drugs, quercetin’s vina score is the highest (Tables 13, 14) (Fig. 10) for signaling proteins20. EGFR promotes tumorigenesis by regulating epithelial tissue development and homeostasis. β-arrestin regulates cell proliferation, migration, promotes cell invasion, sends anti-apoptotic survival signals, influences tumor growth rate, metastatic potential, angiogenesis, and drug resistance. CXCL12, secreted by carcinoma-associated fibroblasts (CAFs), directly stimulates tumor growth by acting through CXCR4, which is articulated by BC cells and promotes invasiveness. During tumor development, CXCL12 also acts as a chemo-attractant. In malignant tumors, its expression promotes and contributes for tumor growth and metastasis. CCR5 may indirectly affect cancer development by regulating the antitumor immune response20.
Table 13: Signaling protein target classes used in the present study
|
Sl. No. |
Protein molecule |
RCSB id |
Length |
Resolution |
Vina score of the drugs used |
|
1. |
Chimera protein of C-C chemokine receptor type 5 and Rubredoxin |
4MBS |
414 |
2.71 Å |
A:-8.6;C:-7.3;Q:-7.9 |
|
2. |
epidermal growth factor |
1JL9 |
51 |
3.00 Å |
A:-6.2;C:-6.4;Q:-6.4 |
|
3. |
Beta-arrestin-2 |
6K3F |
377 |
2.30 Å |
A:-8.9;C:-8.2Q:-9 |
|
4. |
Stromal cell-derived factor 1 |
2NWG |
68 |
2.07 Å |
A:-6.6;C:-5.9;Q:-6.9 |
|
5. |
Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-2 (HER 2) |
5O4G |
606 |
3.00 Å |
A:7.4;c:8;q:8.4 |
Table 14: Contact amino acids and varieties of bonds between the target and the ligand molecules belong signaling involved in breast cancer.
|
PDB |
Contact residues and bond pattern |
||
|
Anastrazole |
Capecitabine |
Quercetin |
|
|
4MBS |
TYR37TRP86TYR89 THR284 MET287 Hydrogen (4), ionic (2), weak hydrogen |
TYR108PHE109 Hydrogen (3), hydrophobic (9), weak hydrogen (1) |
LEU33TYR37 Hydrogen (4), |
|
2NWG |
LEU29ASN30 Weak hydrogen (3), |
LYS24HIS25LYS43 Weak hydrogen (1), |
LYS1VAL3SER ARG41 Weak (1), hydrogen (8), |
|
6K3F |
ASP27ARG170 Ionic (2), cation-pi (1), |
ASP27ARG170HIS THR300ASN301 Ionic (1), |
ASN225SER226 Ionic (2), |
|
1JL9 |
TYR44ILE38GLY Pi-pi (1), ionic (1), |
ARG45CYS6PRO7 Hydrogen (6), |
CYS6PRO7LEU8SER Weak hydrogen (1), |
|
5O4G |
THR5GLY6THR7 36GLN59GLN84 Hydrogen (6), hydrophobic (8), ionic (2), weak hydrogen (2) |
ASP163THR164 Hydrogen (7), |
THR1VAL3CYS4THR Hydrogen (11), hydrophobic (8), weak hydrogen (8) |
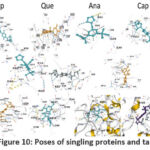 |
Figure 10: Poses of singling proteins and targets |
Transcription factors as targets
Vina score of quercetin seemed to be the highest when compared to the three drugs (Tables 15, 16 and Fig. 11) for transcription factors20. Drug activation of ER beta significantly inhibits cancer cell growth. HIF-1 activates cancer cell survival genes and allows them to grow in the hostile hypoxic tumor environment. Increased tumor HIF-1alpha has been linked to aggressive tumor growth, angiogenesis, and poor prognosis. Rb C-terminal domain (RbC) is required for growth inhibition. Above 66% of breast carcinomas express Erα, and majority ER+ tumors also express progesterone receptors (PRs). Chemotherapy is rendered less effective due to ER mutations. Patients with advanced disease condition will have a high mutation rate. NFκB encourages the development of an autonomous (hormone-independent), aggressive, high-grade, and late-stage tumor phenotype. The ERα’s anti-cancer properties are based on the sealing of its ligand binding domain20.
Table 15: Transcription factor target classes used in the present study
|
Sl.No. |
Protein molecule |
RCSB id |
Length |
Resolution |
Vina score of the drugs used |
|
1. |
Estrogen receptor |
7JHD |
251 |
2.40 Å |
A:-7.3;C:-7.7;Q:-8.3 |
|
2. |
Estrogen receptor |
6SBO |
260 |
1.48 Å |
A:-7.9;C:-7.1;Q:-8.4 |
|
3. |
Transcription factor Dp-1 |
2AZE |
155 |
2.55 Å |
A:-7.1;C:-7.2;Q:-7.7 |
|
4. |
Protein (nuclear factor kappa-b (Nf-kB) |
1NFK |
325 |
2.30 Å |
A:-8.3;C:-8.4;Q:-9.6 |
|
5. |
Progesterone receptor |
4OAR |
258 |
2.41 Å |
A:-7.9;C:-7.8;Q:-8.1 |
|
6. |
Estrogen receptor beta |
2I0G |
257 |
2.50 Å |
A:-8.6;C:-7.8;Q:-8.8 |
|
7. |
Estrogen receptor beta |
5TOA |
249 |
2.50 Å |
A:-7.4;C:-7.3;Q:-8.9 |
|
8. |
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha inhibitor |
1YCI |
349 |
2.70 Å |
A:-8.1;C:-6.7;Q:-7.4 |
|
9. |
Stromal cell-derived factor 1 alpha |
2J7Z |
68 |
1.95 Å |
A:-6.2;C:-5.9;Q:-6.7 |
Table 16: Poses, contact amino acids and varieties of bonds between the target and the ligand molecules belong to transcription factors involved in breast cancer.
|
PDB |
Contact residues and bond pattern |
||
|
Anastrazole |
Capecitabine |
Quercetin |
|
|
5TOA |
GLU276 TYR397LYS401 Hydrophobic (7), |
GLU276PRO HIS279VAL280 TYR397LYS401 Pi-pi (2) Hydrogen (4), |
MET295LEU 299LEU301ALA302 Hydrogen (8), |
|
1YCI |
TYR93PHE100 Ionic (4), hydrophobic (10), |
TYR102TYR LEU186LEU188 Pi-pi (1), cation-pi (1), |
TYR93SER94 LEU101TYR102 TRP296 Ionic (1), hydrophobic (13) |
|
2I0G |
MET295LEU298 Ionic (2), hydrophobic |
GLU276 Ionic (1), |
MET295LEU Ionic (1), |
|
1NFK |
BLYS249VAL251 269ASP271 Pi-pi (6), cation-pi (2) |
ARG161GLY PRO165GLY166 Pi-pi (13), ionic (3), |
GLY162 165GLY166 Pi-pi (9), ionic (3), |
|
2AZE |
PHE233LEU259 261ILE262ASP295 Weak hydrogen (2), |
PHE233VAL PRO260PHE261 Hydrogen (6), |
PHE233VAL PRO260ASP295 Hydrogen (6), |
|
6SBO |
MET343LEU346 Hydrophobic (18), |
MET343LEU LEU349ALA350 Hydrogen (4), |
MET343LEU 347LEU349ALA Hydrogen (4), |
|
4OAR |
GLU695 Hydrophobic (12), |
GLU276 HIS279GLU305 Pi-pi (2), |
PRO696ASP 698ILE699TYR Weak hydrogen (2), |
|
7JHD |
MET343LEU THR347LEU349 Ionic (1), |
LEU320 PRO325ILE326 Cation-ion(2), |
MET343LEU 346THR347LEU349 Pi-pi (2), ionic (1), |
|
2J7Z |
VAL3 PRO10 LEU29ASN30 ASN46 Hydrophobic (11) |
ARG20ALA21 43GLU60TYR61LYS Hydrophobic (11), |
VAL3 CYS9PRO10 23LYS24 LYS43 Hydrogen (9), |
 |
Figure 11: Binding poses of transcription factors in breast cancer cell lines with the ligands |
Transferases as targets
Quercetin’s vina score is highest, with the proteins belonging to transferases (Table 17, 18) (Fig. 12a and 12b). Somatic genetic alterations most frequently activate CDK4 and cyclin D1 in a variety of tumor types. CDK4 is a genetically validated therapeutic target, since CDK4/ cyclin D1 pathway is important in oncogenesis. The estrogen receptor (ER) is overexpressed in breast cancer. In ER alpha-positive human breast cancer cells, stromal cell-derived factor 1 (SDF-1), (cytokine stimulator for growth) is a genuine goal of estrogen’s action. Cyclin-Dependent Kinases (CDKs) have been proposed as novel and promising target for cancer therapy. These, in conjugation with cyclins, show an important role in cell cycle advancement. CDK dysregulation results in increased cell propagation, has been established in a number of cancers, no exception to BC. CDK1 selective inhibition is linked to potent anti-cancer outcomes either combined with other therapeutics or alone. VEGF promotes vessel proliferation, invasion and survival and endothelial cell proliferation. Tumor cell shape, proliferation, motility, progression and metastasis depend on overexpressed Rho-associated protein kinase 1. Cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) regulate cell cycle, apoptosis, transcription and neuronal functions. EphA2 Receptor Protein Kinase regulates cytoskeleton dynamics, cell adhesion, proliferation, differentiation, and metastasis. JAK2 regulates gene expression in the G1 cell cycle, proliferation, oncogenesis, anti-apoptosis, angiogenesis and metastasis. EphA2 tyrosine kinase is involved in angiogenesis, cancer, and inflammation20.
Table 17: Transferase target classes used in the present study
|
Sl. No. |
Protein molecule |
RCSB id |
Length |
Resolution |
Vina score of the drugs used |
|
1. |
Cell division protein kinase 2 |
2BHH |
298 |
2.60 Å |
A:-8.8;C: 7.9;Q:-8.9 |
|
2. |
Vascular endothelial growth factor A |
4KZN |
104 |
1.71 Å |
A:-5.5;C:-5.8;Q:-6.0 |
|
3. |
Rho-associated protein kinase 1 |
3TWJ |
410 |
2.90 Å |
A:-8.8;C:-7.5;Q:-8.9 |
|
4. |
Epidermal growth factor receptor |
2ITX |
327 |
2.98 Å |
A:-7.6;C:-7.1;Q:-8 |
|
5. |
Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase FKBP5 |
4DRH |
144 |
2.30 Å |
A:-8.4;C:-8.5;Q:-8.4 |
|
6. |
Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1 |
1S9J |
341 |
2.40 Å |
A:-6.7;C:-7.5;Q:-8.6 |
|
7. |
Nicotinamide phosphoribosyl transferase |
2GVG |
491 |
2.20 Å |
A:-8.4;C:-8.8;Q:-10.1 |
|
8. |
Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit, gamma isoform |
2A5U |
966 |
2.70 Å |
A:-9.6;C:-7.8;Q:-9.3 |
|
9. |
Mitogen-activated protein kinase 14 |
4FA2 |
383 |
2.00 Å |
A:-8.7;C:-7.8;Q:-9.2 |
|
10. |
Ephrin type-A receptor 2 |
1MQB |
333 |
2.30 Å |
A:-7.6;C:-7.2;Q:-7.5 |
|
11. |
epidermal growth factor receptor |
1M17 |
333 |
2.60 Å |
A:-7.7;C:-6.7;Q:-8.4 |
|
12. |
Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 |
1YWN |
316 |
1.71 Å |
A:-7.2;C:-6.9;Q:-7.9 |
|
13. |
v-akt murine thymoma viral oncogene homolog 1 (AKT1) |
3MV5 |
342 |
2.47 Å |
A:-8.4;C:-8;Q:-8.2 |
|
14. |
Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase |
3OAW |
966 |
2.75 Å |
A:-9.6;C:-7.6;Q:-8.3 |
|
15. |
Inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-B kinase subunit beta |
4KIK |
677 |
2.83 Å |
A:-7.9;C:-7.4;Q:-8.5 |
|
16. |
v-akt murine thymoma viral oncogene homolog 1 (AKT1) |
3OCB |
341 |
2.70 Å |
A:-8.2;C:-8.1;Q:-8.4 |
|
17. |
Epidermal growth factor receptor |
4WKQ |
330 |
1.85 Å |
A:-7.2;C:-6.6;Q:-8.3 |
|
18. |
Ephrin type-A receptor 4 |
4M4P |
518 |
2.08 Å |
A:-6;C:-6.4;Q:-6.7 |
|
19. |
RAC-alpha serine/threonine-protein kinase |
3CQW |
342 |
2.00 Å |
A:-8.5;C:-7.9;Q:-8.5 |
|
20. |
Cell division protein kinase 6 |
3NUP |
307 |
2.60 Å |
A:-8.3;C:-6.8;Q:-8.6 |
|
21. |
Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 |
1DI8 |
298 |
2.20 Å |
A:-9.3;C:-7.9;Q:-10 |
|
22. |
cyclin D1-cyclin-dependent kinase 4 (CDK4) (G1/S-Specific cyclin-D1) |
2W96 |
271 |
2.30 Å |
A:-7.9,C:-7.4,Q:-9.2 |
|
23. |
Cyclin-dependent kinase 6 |
1XO2 |
254 |
2.90 Å |
A:-9.2;C:-8;Q:-10.6 |
|
24. |
Epidermal growth factor receptor |
2J6M |
327 |
3.10 Å |
A:-7.9;C:-7.2;Q:-8.4 |
|
25. |
Protein (CDK2 human) |
1BUH |
298 |
2.60 Å |
A:-7.7;C:-7.8;Q:-8.3 |
|
26. |
Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-2 |
3PP0 |
338 |
2.25 Å |
A:-8.7;C:-9.2;Q:-9.4 |
|
27. |
Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 |
2OH4 |
316 |
2.05 Å |
A:-7.5;C:-7.4;Q:-9.6 |
|
28. |
RAC-alpha serine/threonine-protein kinase |
3O96 |
446 |
2.70 Å |
A:-9.9;C:-8.1;Q:-9.7 |
|
29. |
RAC-alpha serine/threonine-protein kinase |
3CQU |
342 |
2.20 Å |
A:-8;C:-7.9;Q:-9.2 |
|
30. |
RAC-alpha serine/threonine-protein kinase |
3OW4 |
341 |
2.60 Å |
A:-7.8;C:-7.3;Q:-8.1 |
|
31. |
Epidermal growth factor receptor |
5FED |
328 |
2.65 Å |
A:-8.2;C:-7;Q:-7.9 |
|
32. |
Ephrin a2 (epha2) receptor protein kinase |
5NKA |
306 |
1.38 Å |
A:-7;C:-6.6;Q:-7.9 |
|
33. |
Glutathione S-transferase P |
2A2R |
210 |
1.40 Å |
A:-7.3;C:-7.1;Q:-7.9 |
|
34. |
Ribosomal protein S6 kinase alpha-3 |
3G51 |
325 |
1.80 Å |
A:-7.8; C:-7.5;Q:-8.3 |
|
35. |
Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK2 |
3KRR |
295 |
1.80 Å |
A:-7.9;C:-7.5;Q:-9.1 |
|
36. |
Cyclin-dependent kinase 1 |
4YC3 |
302 |
2.7 Å |
A:-7.6;C:-7.1;Q:-9.5 |
|
37. |
EphA2 ligand-binding domain (LBD) |
6NJZ |
187 |
1.90 Å |
A:-7.4; C:-7.8; Q:-8.4 |
Table 18: Contact amino acids and varieties of bonds between the target and the ligand molecules belong to transferases involved in breast cancer.
|
PDB |
Contact residues and bond pattern |
||
|
Anastrazole |
Capecitabine |
Quercetin |
|
|
2W96 |
LEU6CYS8ILE Hydrophobic (11),
|
ILE12GLY13VAL Hydrophobic (7), |
ILE12GLY15ALA16T ASP158 Weak hydrogen (7), |
|
3TWJ |
ILE82 103MET128 Hydrophobic (14),
|
ILE82 85VAL90LEU92 Hydrophobic (20), |
ILE82 VAL90 102ALA103LYS105 Hydrophobic (18), |
|
1BUH |
ILE10GLY11GLU Ionic (3), hydrophobic
|
ILE10 14VAL18TYR19 PHE80GLU81 Ionic (2), |
ILE10GLY11GLU Ionic (1), |
|
4YC3 |
GLN184ALA R223MET224 Hydrogen (7),
|
GLU181GLU ALA185VAL186 Hydrogen (2),
|
LEU180GLU181GL Hydrogen (10), |
|
4KZN |
GLU38 73ASN75SER Ionic (1), hydrogen,
|
CYS57GLY58 Hydrogen (7), |
CYS26GLY59CYS60C Hydrogen (6), |
|
1XO2 |
ILE19GLY20 GLY25VAL27 Hydrophobic (13), |
ILE19 41LYS43GLU GLU99HIS100 Hydrophobic (13), |
ILE19 GLY20VAL27 Hydrophobic (12), |
|
4DHR |
TYR57 PHE67 Ionic (1), hydrophobic |
TYR57ASP68 PHE77PRO GLU2032SER PHE2108 Hydrophobic (17), |
ASP68HIS71PHE77 TYR2105PHE2108 Ionic (2), |
|
2ITX |
LEU718VAL726ALA LEU844THR854 Ionic (3), hydrophobic
|
ALA702LEU703 PRO1019 Ionic (1), |
LEU718GLY719VAL Ionic (1), |
|
2BHH |
ILE10 GLY11 ALA31LYS33VAL Ionic (2), hydrophobic (17),
|
ILE10GLY11VAL Ionic (1),
|
ILE10GLY11GLU12 Ionic (2), |
|
1S9J |
LEU74GLY75ALA76 Ionic (1), hydrophobic (11),
|
LEU74GLY75 Ionic (1), |
LEU74GLY75ALA76 Ionic (1), |
|
2GVG |
ASP192PHE193GLY Ionic (12), cation-pi (1)
|
ASP16TYR18 Ionic (4), |
ASP16TYR18ARG392 Ionic (4),
|
|
3MV5 |
GLY157LYS158 Pi-pi (1), ionic (5), |
LYS158GLY159 Ionic (3), |
GLY157LYS158GLY Ionic (4),
|
|
1MQB |
ILE619GLY620 Ionic (3), hydrophobic
|
ILE619GLY622GLU Hydrophobic (6),
|
ILE619GLY622GLU Ionic (1), |
|
3NUP |
ILE19GLY20VAL ASP163 Ionic (4)
|
ILE19GLY20VAL27 Ionic (2), |
ILE19VAL27ALA41 Ionic (2), |
|
1M17 |
LEU694PHE699 Ionic (4), hydrogen (5), |
LEU694VAL702 Hydrophobic (7), |
LEU694VAL702ALA Ionic (2), |
|
1YWN |
LYS866GLU883 Ionic (8), hydrogen (1),
|
TRP1094TYR1104 Hydrophobic (7),
|
LEU838GLY839VAL Ionic (1), |
|
4WKQ |
LEU718GLY719 MET766CYS775 THR854 Hydrophobic (11),
|
LEU718GLY719 Ionic (1), hydrophobic (11), |
LEU718GLY719VAL Hydrophobic (6), |
|
2J6M |
LEU718PHE723 ASN842LEU ASP855 Ionic (5), |
LEU718VAL726LYS Ionic (2), hydrogen (5), |
LEU718GLY719VAL Ionic (2), |
|
1DI8 |
ILE10GLY11GLU Ionic (2), |
ILE10VAL18ALA Ionic (1) |
ILE10VAL18ALA31 Hydrophobic (15), |
|
3KRR
|
LEU855GLY856 Hydrogen (3),
|
LEU855GLY856 Hydrophobic (11), |
LEU855VAL863ALA Hydrophobic (8),
|
|
4FA2 |
VAL30VAL38 LYS53ILE84 Hydrophobic (14),
|
VAL30VAL38ALA51 Ionic (1), |
VAL30VAL38ALA51 Hydrophobic (14), |
|
5NKA |
ILE619VAL627 SER756ASP757 Hydrophobic (8), |
ILE619VAL627ALA Hydrophobic (13), |
ASP708LEU716TRP Hydrophobic (10), |
|
3G51 |
LEU74GLY75GLN Hydrophobic (11), |
LEU74GLY75GLN Hydrophobic (9), |
LEU74GLY75GLN76 Hydrophobic (15), |
|
4KIK |
ARG105CYS114 Ionic (2),
|
PHE219VAL244SER2 GLN432 Ionic (1),
|
ARG105LEU108ASN Ionic (2), hydrophobic (3), |
|
3OW4 |
LEU156GLY157 Ionic (7), pi-pi (1) |
LEU156GLY157VAL Ionic (2), |
LEU156GLY157LYS Ionic (1), |
|
4M4P |
ILE336SER337 Hydrophobic (3), |
GLU451THR453TYR Hydrophobic (7), |
ARG37SER38GLN40 Ionic (2) hydrophobic |
|
6NJZ |
TRP43LEU44 Pi-pi (1), |
GLY39GLU40LEU41 ASN133MET10 Hydrophobic (7), |
TRP43LEU44THR45 Pi-pi (1), hydrophobic
|
|
2A5U |
LEU657HIS658 Hydrophobic (12),
|
TRP201PRO208TYR Hydrophobic (18),
|
MET804PRO810TRP Hydrophobic (18), |
|
2J6M |
LEU718PHE723 Ionic (5), |
LEU718VAL726LYS728 Ionic (2), |
LEU718GLY719VAL Ionic (2), |
|
2OH4 |
ASP1026ARG1030 Ionic (4), |
ASP1026ARG1030 PRO1066 Ionic (2), |
ASP1026ARG1030A Ionic (1), hydrophobic (15), |
|
3CQU |
LEU156GLY157 Ionic (3),
|
THR160LYS179 Ionic (2),
|
LEU156GLY157LYS1 Ionic (2), |
|
5FED |
LEU718GLY719 Ionic (1),
|
LEU718VAL726 Ionic (1),
|
LEU718GLY719VAL Hydrophobic (9), |
|
2A2R |
TYR7PHE8VAL10 Hydrophobic
|
ARG13GLN51LEU Ionic (2), |
ARG74TYR79GLY80 Ionic (2), |
|
3OCB |
GLY159THR160 Ionic (5), |
LYS158GLY159PHE Ionic (4), |
LEU156GLY157LYS Ionic (2), |
|
3O96 |
ASN53GLN79TRP Ionic (1),
|
ASN54GLN79TRP80THR81 Hydrophobic (11),
|
ASN54GLN79TRP80 Hydrophobic (9), |
|
3PP0 |
LEU726VAL734 Ionic (1),
|
LEU726GLY727S Ionic (1), |
LEU726SER728GLY Ionic (1), |
|
3OAW |
TRP201LEU LEU661ARG690 GLU880 Ionic (1), |
SER806LYS807LYS808 Pi-pi (2),
|
ALA889LYS890GLN Pi-pi (3), |
|
3CQW |
LYS158GLY159 Ionic (5), weak (3), |
LYS158GLY159P Hydrophobic (12), hydrogen (18), ionic (5), weak (4) |
LEU156GLY157 ARG4 Weak (3), |
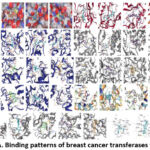 |
Figure 12: A. Binding patterns of breast cancer transferases with drugs.
|
 |
Figure 12: B. Binding patterns of breast cancer transferases with drugs.
|
The EphA4 receptor, (Eph receptor tyrosine kinases family member), is a well-known cell functions (cell adhesion, invasion and migration) regulator. These events occur due to modification of actin cytoskeleton organization. In a variety of cell types, FKBP1 is identified as NF-κB signaling regulator (nuclear factor binding near the κ light-chain in B-cells). As a result, FKBP51 is proposed as a target to treat NF-κB-mediated inflammation and cancer. Cancer relies heavily on p38 activity. p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) are important in cancer cellular responses, proliferation, survival, cell cycle and migration. The growth factor-activated Ser/Thr kinase p90 ribosomal protein kinase 2 (RSK2) is involved in cell multiplication and tumor promoter-induced cell transformation. Cell growth, motility, survival, metabolism, and angiogenesis are all regulated by human PI3K gamma. CDKs (Cyclin-dependent kinases) play critical role in cell cycle progress and RNA transcription. GSTP-silencing effectively suppressed cell proliferation while not completely killing the cells. GSTP performs a non-enzyme function in signal transduction via a protein-protein interaction with JNK that guards cancer cells from apoptosis. AKT1 kinase (AKT kinase – a serine/threonine-protein kinase) regulates many signaling downstream pathways participate in cell proliferation, metabolism, survival, growth, and angiogenesis. It belongs to the most commonly triggered multiplying and surviving pathways in cancer. Autophagy and metabolism are both regulated by EGFR. Non-canonical functions are commonly brought by cellular and environmental stresses. These ‘stress pathways’ are activated in cancer cells and benefit them to survive and resist to therapy. Human IkB kinase beta (IkappaB kinase or IKK) is involved cell proliferation regulation, apoptosis control, angiogenesis promotion and invasion/metastasis stimulation. EGFR regulates EMT (epithelial-mesenchymal transition), cell migration and invasion. Its high expression is a sole predictor of poor diagnosis in Inflammatory Breast Cancer (IBC) and by rewiring apoptotic signaling networks in Triple Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC), its inhibition improves chemosensitivity20.
Upregulation of intra-cellular signaling paths, PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway, considering an example, promotes cancer growth and development by driving cellular proliferation, resulting in un-checked cell growth. VEGFR-2 regulates tumor angiogenesis directly. The VEGF/VEGFR-2 system is essential for cancer cell division and survival as an autocrine/paracrine process. Breast cancers overexpress the HER2 receptor, and HER2 overexpression is linked to aggressive tumor growth and metastasis. Cyclin-dependent kinase 6 (CDK6) is vital in cell cycle progression regulation. Recently, it was shown that CDK6 plays a transcriptional lead in tumor angiogenesis. NMPRTases are important in the salvage pathway of NAD+ biosynthesis. FK866 (a potent NMPRTase inhibitor) reduces cellular NAD+ levels and induces apoptosis in tumors. The MAPK signaling pathway connects extracellular signals to the intracellular process that regulates growth, proliferation, migration, and apoptosis20.
Docking simplified the analysis of protein-ligand interactions. Hydrogen, weak hydrogen, hydrophobic, ionic, pi-pi sticking, covalent, and van der Waals interactions are examples of interactions23. The study highlights the main bond pattern viz., hydrogen, hydrophobic, in addition to weak hydrogen bonds and limited cation-pi, pi-pi sticking, and ionic interactions. These bonds have a significant correlation with the vina score of the respective drug and its counterpart ligand. Furthermore, the energies were high due to the increased hydrogen and hydrophobic interactions.
Among the transferase target classes investigated in this study, cyclin-dependent kinase had the highest vina score with quercetin when compared to the other two drugs. The first higher class is (1XO2), which is followed by (1DI8), which has more hydrogen and hydrophobic bonds, considered as predominant in this class. Chronic inflammation is distinguished by the production of reactive nitrogen and oxygen species. These species initiate tumorigenesis, inhibit apoptosis, promote hyper cellular proliferation, and promote angiogenesis. These conditions cause the NFkB pathways to be activated. Although NFkB is required for normal mammary cell morphogenesis, irregular expression has been observed in BC cells24. A good idea is to target NFkB to control cell proliferation. The molecules studied were (1NFK), but with a vina score of -9.6, quercetin came out on top. The mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway regulates several processes including tumor development. In conjugation with the MAPK cascade, beta-arrestin proteins target G protein-couple receptors and promote tumor progression25. Targeting beta-arrestin is a good choice, and in this study, quercetin effectively targeted (6K3F) beta-arrestins. Estrogen receptors aid in the binding of estrogen, which is required for cell proliferation, and blocking these receptors aids in the supervision of cancer disease. Again quercetin has a strong affinity for the estrogen receptor (4PP6).
In cancer prevention, redox maintenance in cell is critical. In aerobic conditions, ROS (reactive oxygen species) influence lipid, protein and DNA metabolism and function. Changes in DNA and proteins are important in cancer pathophysiology. Oxidoreductases are the enzymes that maintain ROS and neutralize oxidative stress26. Chemoresistance is linked to Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2 and is linked to injury, proliferation, and inflammation 27,28. The Cytochrome P450 1A1/ A2 (CYP1A1/A2) enzyme metabolizes both xenobiotics and endogenous substrates. These enzymes are involved in the activation of pro-carcinogens (estradiol and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons)29.
The targeted proteins (3LN1, 6DWN and 2HI4) bound to quercetin with a highest vina score than the other two drugs. The alpha enzyme, DNA topoisomerase II, changes the topology of DNA during transcription. The enzyme primarily catalyzes the temporary breaking (transient) and rejoining of the two duplex DNA strands, there by altering the topology30. With the highest vina score of the three drug molecules, Quercetin targeted this enzyme. Matrix metalloproteinase-9 degrades extracellular matrix proteins, and surface plasma proteins, allowing them to be released to the cell surface. It plays a wide range of roles in invasion, angiogenesis, and metastasis. Targeting MMP-9 is the best option, and present work highlighted that quercetin was the best at it. Myeloid cell leukemia-1, a close relative of B-cell lymphoma 2, promotes survival and invasion of cancer cells, making it an important chemotherapeutic target. The highest vina score of (-8.5) was achieved by quercetin.
The study concluded that cancer metabolism is largely reliant on amino acids, which are aided by the TCA cycle. Amino acid derivatives promote cancer cell progression and improve cells’ ability to metastasize. Amino acid catabolism (metabolic intermediates) influences the survival and growth of cancer cells. Targeting the enzymes with the amino acids such as leucine, valine, and glutamine (TCA cycle fuel); asparagine, glycine, and glutamine (nucleotide biosynthesis); serine, methionine, glycine (methionine-folate cycle); glutathione, cysteine, and glycine (to maintain redox balance); methionine, serine, and glycine (DNA and histone methylation) reduces the cancer cell proliferation and tumor burden31. More vina score correlates with more hydrogen and hydrophobic interactions.
Conclusion
It confirms that, out of the three drugs tested, the natural compound quercetin establishes the most effective in targeting and controlling the BC cells, in line with our in vitro work10. When BC cell lines were fed with quercetin, anastrozole, and capecitabine, both independently and in combination, a decrease in cell viability and increase in apoptosis percentage at low doses of Quercetin10 was noted. Because quercetin is chemoprotective and radioprotective to healthy/normal cells, it can be used during cancer treatment.
Acknowledgement
Author is grateful to the Academy, Sri Devaraj Urs Acadmy of Higher Education and Research for providing the facility to carry out this docking study. Author is mentioning her gratitude to Dr. Prashanthi K., Assistant Professor, Department of Biotechnology, M.S. Ramaiah University of Applied Sciences, Bengaluru.
Conflict of Interest
There is no conflict of interest.
Funding Sources
There is no funding Sources.
References
- Lafourcade A, His M, Baglietto L, Boutron-Ruault M. C, Dossus L and Rondeau V. Factors associated with breast cancer recurrences or mortality and dynamic prediction of death using history of cancer recurrences: the French E3N cohort. BMC Cancer., 2018; 9:18(1):171. http://doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-4076-4. PMID: 29426294; PMCID: PMC5807734.
CrossRef - Cava E, Marzullo P, Farinelli D, Gennari A, Saggia C, Riso S, et al. Breast Cancer Diet “BCD”: A Review of Healthy Dietary Patterns to Prevent Breast Cancer Recurrence and Reduce Mortality. Nutrients., 2022; 21:14(3):476. http://doi: 10.3390/nu14030476. PMID: 35276833; PMCID: PMC8839871.
CrossRef - Jia T, Liu Y, Fan Y, Wang L and Jiang E. Association of Healthy Diet and Physical Activity With Breast Cancer: Lifestyle Interventions and Oncology Education. Front. Public Health., 2022; 23:10:797794. http://doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.797794. PMID: 35400043; PMCID: PMC8984028.
CrossRef - Abdullahi S. H, Uzairu A, Shallangwa G. A, Uba S and Umar B. In-silico activity prediction, structure-based drug design, molecular docking and pharmacokinetic studies of selected quinazoline derivatives for their antiproliferative activity against triple negative breast cancer (MDA-MB231) cell line. Bull. Natl. Res. Cent., 2022; 46:2. https://doi.org/10.1186/s42269-021-00690-z
CrossRef - David C. F and Lyubomir T.V. Targeting protein-protein interactions for cancer therapy. J. Mol. Med., 2005; 83: 955-963.
CrossRef - Md Mahmudul Hasan, Zidan Khan, Mohammed Salahuddin Chowdhury, Md Arif Khan, Mohammad Ali Moni, et al. In silico molecular docking and ADME/T analysis of Quercetin compound with its evaluation of broad-spectrum therapeutic potential against particular diseases. Informatics in Medicine Unlocked., 2022; 29. 100894. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imu.2022.100894
CrossRef - Wang R, Yang L, Li S, Ye D, Yang L, Liu Q, et al. Quercetin Inhibits Breast Cancer Stem Cells via Down regulation of Aldehyde Dehydrogenase 1A1 (ALDH1A1), Chemokine Receptor Type 4 (CXCR4), Mucin 1 (MUC1), and Epithelial Cell Adhesion Molecule (EpCAM). Med. Sci. Monit., 2018; 24:412-420. http://doi: 10.12659/msm.908022. PMID: 29353288; PMCID: PMC5788241.
CrossRef - Barros-Oliveira M. D. C, Costa-Silva D. R, Andrade D. B, Borges U. S, Tavares C. B, et al. Use of anastrozole in the chemoprevention and treatment of breast cancer: A literature review. Rev. Assoc. Med. Bras. (1992). 2017; 63(4):371-378.http:// doi: 10.1590/1806-9282.63.04.371. PMID: 28614542.
CrossRef - Varshavsky-Yanovsky A.N and Goldstein L.J. Role of Capecitabine in Early Breast Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol., 2020; 38(3):179-182. http://doi: 10.1200/JCO.19.02946. Epub 2019 Dec 5. PMID: 31804861; PMCID: PMC6968794.
CrossRef - Rani Inala M. S and Pamidimukkala K. Amalgamation of quercetin with anastrozole and capecitabine: A novel combination to treat breast and colon cancers-An in vitro study. J. Can. Res. Ther. [Epub ahead of print] http://www.cancer journal.net/preprintarticle.asp?id=322160
- Daina A, Michielin O and Zoete V. SwissADME: a free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules. Sci Rep. 2017; 7:42717. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep42717Gfeller D, Grosdidier A, Wirth M, Daina A, Michielin O, Zoete V.
CrossRef - https://www.molinspiration.com/docu/miscreen/druglikeness.html
- Lipinski C. A, Lombardo F, Dominy B.W and Feeney P.J. Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings. Adv. Drug Deliver. Rev., 2001; 46: 3–26
- SwissTargetPrediction: a web server for target prediction of bioactive small molecules. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Jul;42(Web Server issue):W32-8. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku293. Epub 2014 May 3. PMID: 24792161; PMCID: PMC4086140.
CrossRef - Antoine Daina, Olivier Michielin and Vincent Zoete. SwissTargetPrediction: updated data and new features for efficient prediction of protein targets of small molecules, Nucleic Acids Research. 2019; 47, W357–W364, https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz382
CrossRef - https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/
- https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/#query=Anastrozole
- https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/#query=Capecitabine
- https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/#query=Quercetin
- Berman H.M, Westbrook J, Feng Z, Gilliland G, Bhat T.N, Weissig H, etal. The Protein Data Bank Nucleic Acids Research. 2000; 28: 235-242.
CrossRef - Yang Liu, Xiaocong Yang, Jianhong Gan, Shuang Chen, Zhi-Xiong Xiao, Yang Cao, CB-Dock2: improved protein–ligand blind docking by integrating cavity detection, docking and homologous template fitting, Nucleic Acids Research., 2022; 50 W1: W159–W164, https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkac394
CrossRef - Lipinski C. A. Lead- and drug-like compounds: the rule-of-five revolution. Drug Discov. Today Technol., 2004;1(4):337-41. doi: 10.1016/j.ddtec.2004.11.007. PMID: 24981612.
CrossRef - Pantsar T and Poso A. Binding Affinity via Docking: Fact and Fiction. Molecules. 2018;23(8):1899. doi: 10.3390/molecules23081899. PMID: 30061498; PMCID: PMC6222344.
CrossRef - Wang W, Nag S. A and Zhang R. Targeting the NFκB signaling pathways for breast cancer prevention and therapy. Curr. Med. Chem., 2015;22(2):264-89. doi: 10.2174/0929867321666141106124315. PMID: 25386819; PMCID: PMC6690202.
CrossRef - Song Q, Ji Q and Li Q. The role and mechanism of β‑arrestins in cancer invasion and metastasis (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med., 2018; 41(2):631-639. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2017.3288. Epub 2017 Nov 27. PMID: 29207104; PMCID: PMC5752234.
- Srijiwangsa P and Na-Bangchang K Roles of NAD (P) H-Quinone Oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1) On Cancer Progression and Chemoresistance. J. Clin. Exp. Oncol., 2017; 6:4. doi: 10.4172/2324-9110.1000192
CrossRef - Hla T and Neilson K. Human cyclooxygenase-2 cDNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A., 1992;89(16):7384-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7384. PMID: 1380156; PMCID: PMC49714.
CrossRef - Tazawa R, Xu X. M, Wu K. K and Wang L.H. Characterization of the genomic structure, chromosomal location and promoter of human prostaglandin H synthase-2 gene. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 1994;203(1):190-9. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.2167. PMID: 8074655.
CrossRef - Rodriguez M and Potter D.A. CYP1A1 regulates breast cancer proliferation and survival. Mol Can Res. 2013; 11(7): 780-792. https://doi.org/10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-12-0675
CrossRef - https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/7153
- Lieu E.L, Nguyen T, Rhyne S. et al. Amino acids in cancer. Exp. Mol. Med., 2020; 52,15–30. https://doi.org/10.1038/s12276-020-0375-3
CrossRef








