Chagi Venkatesh and S. B. Puranik
and S. B. Puranik
Prist University, Thanjavur, Tamilnadu, India.
Corresponding Author E-mail: Venkatesh.chagim@gmail.com
DOI : https://dx.doi.org/10.13005/bpj/1384
Abstract
The purpose of this study is to compare the various regulatory guidelines and consign the self inspection requirements on a single platform and evaluate the requirements to make a common prerequisite. The Importance of self-inspection in pharmaceutical industry is to identify the non-compliance with respect to Manufacturing Practices of production, Quality Control systems, quality assurance procedures, engineering practices, environmental conditions etc., the self-inspection programme is intended to detect and analyze the observations and suggest the necessary corrective actions. Such inspections should be planned with technical persons, having knowledge with respect to the regulatory requirements in that particular field. The inspection shall be conducted for all the departments in the manufacturing facility as per regulatory requirements at least once in year, based on the organization requirements it can be carried out once in quarter or biannually to make sure that all the systems and procedures are under control. Self inspection can be initiated in case of emergencies where the product needs to be withdrawn from the market or recurrence of product failure in the facility or frequent breakdown of the machines or repetitive nature of the packaging components or in case of pre notified regulatory/Customer inspection to the facility etc., The identified observations during audit needs to be discussed during the closure meeting and same shall be updated and linked through CAPA system and follow-up till the closure of these observations.
Keywords
WHO; Schedule M; USFDA; TGA; MHRA; PICS Regulatory Requirements
Download this article as:| Copy the following to cite this article: Venkatesh C, Puranik S. B. Importance of Self - Inspection in Pharmaceutical Industry as Per Various Regulatory Guidelines. Biomed Pharmacol J 2018;11(1). |
| Copy the following to cite this URL: Venkatesh C, Puranik S. B. Importance of Self - Inspection in Pharmaceutical Industry as Per Various Regulatory Guidelines. Biomed Pharmacol J 2018;11(1). Available from: http://biomedpharmajournal.org/?p=19478 |
Introduction
Current study is aimed at requirements of self- inspection as per the different regulatory guidelines viz., WHO, Schedule M of D and C Act, USFDA, MHRA, TGA.
The self inspection is one of the key factors in pharmaceutical industry, to identify known and unknown non-compliance of the process, procedure, equipments, storage conditions, utilities etc., and will be regularized as per the current standard operating procedure or regulatory requirements. This inspection will be conducted atleast once in a year or frequency can be conducted initially once in quarter or month based on the observations and its control, self inspection must be conducted in pharmaceutical industry with sub matter experts of the respective area.
Each of the selected guidelines describes the requirement of self-inspection under the different chapters as below.
WHO describes about the Self-inspection in Annexure 3: 1
Schedule M describes about the Self-inspection in premises Building and facilities of section 15. 2
USFDA (United states of food and drug administration) describes about the Self Inspection in PART 211- sub part B of chapter I3
D. Evaluation Activities 2. Conduct Internal Audits
MHRA (Medicinal Health and Regulatory Agencies) describes about the Self Inspection in Section II – 2EU Guidance on Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) – Self-Inspection 4
TGA (Therapeutic Good and Administration)/PICS (Pharmaceutical Inspection Convention/Pharmaceutical inspection and cooperation scheme) describes about the Self Inspection in CHAPTER 9 Quality Management Self-Inspection5
Self-Inspection
Discussion
Based on the study of self-inspection in the pharmaceutical industry, we infer that as per World Health Organization (WHO), Schedule M of D and C act, USFDA, MHRA and TGA/PICS guidelines, discussion is carried out under different headings for better understanding purpose.
Guidelines Chapters
WHO describes about the Good practices in self-inspection in Annexure-3 of sec 8.1 to 8.9. This section covered in detailed when compared to the other guidelines.
Schedule M part I describes about the self-inspection and quality audit in section 15.1 to 15.3 of Good Manufacturing Practices and Requirements of self-inspection and Quality audit with limited information and does not cover the following topics, a) frequency of self-audit, b) follow-up action and c) Suppliers audit and approval process.2 when compared to the WHO guideline.
USFDA describes about the Self Inspection in PART 211—e-CFR current data as of January 12, 2016 of Chapter 01 — Self Inspection it describes as follows. 3
Evaluation Activities.
Conduct Internal Audits.
MHRA describes about the Self-Inspection in Section II – 2EU Guidance on Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) – Self-Inspection covered under section 9.1 to 9.3 and internal audits (self-inspection) covered in section 2.40 to 2.41.3
TGA /PICS describes about the self-inspection in chapter 9 section 9.1 to 9.3 of Quality management system.5
MHRA/TGA and PICS guidelines are almost identical.
After review of all the above mentioned guidelines self inspection is briefed in detail at WHO when compared to other guideline.
The Process flow chart of self inspection is briefed below.
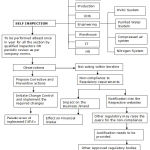 |
Figure 1
|
Summary and Conclusion
The intent of self inspection is to identify the gaps with approved procedure and current regulatory requirements from subject matter expert along with corporate team or from external agencies. The identified observations indicate the overall performance of quality systems and procedures. These observations are discussed in the closure meetings and compliance of those observations through a CAPA tracking system has to be undertaken to ensure that these observations are assessed and closed in timely manner. Such practices will be helpful to give a confidence to the team and management to face any regulatory audits at any point of time. Hence any observations needs to be acted upon priority and block the deviations in real time, This will create the healthy situation for the organization, though initially will have lot of brakes and hiccups , once it is streamlined will get more output with better quality of the product in the long run.
All the inspections reports and its’ compliance reports needs to be documented with supporting evidences which help in monitoring the effectiveness of the implemented CAPAs on routine basis.
If the self inspection and assessment are not in place, it will affect the entire organization, which may lead to critical observations during the Regulatory inspections, general public health will be put to jeopardy, the Brand image of the company and the product will deteriorate which will have financial implications., Hence the management should give priority for self inspection and its compliance on routine and periodic basis, though the regulatory norms suggests it once in a year. Steady and Consistent Quality management systems will augur well for the General public health and the overall well being of the organization,
Conflict of Interest
There is no conflict of interest
Acknowledge
I acknowledge seema gada for her help in composing of this article.
References
- WHO describes about the Self-inspection in Annexure 3-WHO good manufacturing practices for pharmaceutical products: Good practices in Self inspection.
- Schedule M describes about the Self-inspection in PART-I of Good Manufacturing Practices and Requirements of Premises, Plant and Equipment For pharmaceutical Products.
- USFDA describes about the Self-Inspection in PART 211— Current Good Manufacturing Practice for Finished Pharmaceuticals e-CFR data is current as of January 12, Title 21 → Chapter I → Subchapter C → Part 211 → Subpart B → Self Inspection. Evaluation Activities – Conduct Internal Audits. 2016.
- MHRA describes about the Self-Inspection in Section II – 2EU Guidance on Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) – Self-Inspection.
- TGA describes about the Self Inspection in Chapter 9 -Quality Management.
- PICS describes about the Self inspection in Chapter 9- Quality Management.







