Sanjay Prakash, Amit Kumar and K. N. Dwivedi
Department of Dravyaguna, Faculty of Ayurveda Institute of Medical Sciences, Banaras Hindu University Varanasi - 221 005 India.
Abstract
In this study Varuna-Shigru Kwatha has been taken in account to its Ashmarihara action (Lithotryptic). Ayurvedic ancient text mentioned it as lithotryptic action as well as this is used in Urinary Tract Infection. This Kwatha consists of two drugs Varuna and Shigru.Varuna is having Tikta, Kashaya Rasa, Laghu, Ruksha Guna, Ushna Virya and Katu Vipaka. By the virtue of above property this is Kaphavatashamaka and Shigru is having nearly same property viz. Katu(Kshariya), Tikta Rasa,Laghu,Ruksha,Tikshna Guna,Ushna Virya and Katu Vipaka. Due to this property it is Kaphavatashamaka. In various studies it has been proved that this Kwatha prevents the formation of Renal Calculi and breaks the calculi which have been already formed. Apart from this Varuna-Shigru Kwatha is having Antibacterial property due to presence of Pterygospermin in Shigru. This drug is significantly effective in Renal Calculi and UTI.
Keywords
Ayurveda; Kwatha; Ashmarihara; Kshariya; Kaphavatashamaka
Download this article as:| Copy the following to cite this article: Prakash S, Kumar A, Dwivedi K. N. Role of Varuna-Shigru Kwatha in Prevention and Management of Renal Calculi. Biomed Pharmacol J 2010;3(2) |
| Copy the following to cite this URL: Prakash S, Kumar A, Dwivedi K. N. Role of Varuna-Shigru Kwatha in Prevention and Management of Renal Calculi. Biomed Pharmacol J 2010;3(2). Available from: http://biomedpharmajournal.org/?p=1612 |
Introduction
As we know Varuna-Shigru Kwatha is most beneficial in Ashmarichikitsa. The concept of this Kwatha has been started from Yogaratnakara (17th Cent.) for Kaphajashmari fallowed by Bhaishajya Ratnawali (18th Cent.).Kapha dosha is predominant in formation of Renal Calculi and both the drugs of this Kwatha pacify kapha dosha due to Tikta, Kashaya Rasa, Laghu, Ruksha Guna, Ushna Virya and Katu Vipaka of Varuna and Katu(Kshariya), Tikta Rasa,Laghu,Ruksha,Tikshna Guna,Ushna Virya and Katu Vipaka of Shigru and thus helps to remove renal calculi. Antibacterial property due to presence of Pterygospermin in Shigru helps in Urinary Tract Infection (UTI).
Varuna – Shigru Kwatha
According to Ayurvedic Physicians, medicine prepared by boiling a drug on fire is called shrita1.One Pala of coarsely powdered drug is boiled with 16 parts of water in an earthen pot over a mild fire till liquid is reduced to 1/8th of the original quantity2.As Prakshepa Dravyas in Kwatha sugar may be added to the decoction in doses of 1/4, 1/8 and 1/16th part respectively for vata, pitta and kapha disorders. If honey is to be added, it should be in the reverse order of proportion 1/16, 1/8 and 1/4.Pipe fomentation may also be prepared from decoction of leaves of varuna, guduchi, eranda, shigru3.The patients of fever desiring heat should be massaged by the Agurvadya taila4. If there is pain, the patient should be massaged well and then given tub bath in the decoction of varuna, agnimantha, shigru and ashmantaka5.Shigru yush is used to destroy the ashmari6.This varunadi gana mitigates kapha and medas, cures headaches, abdominal tumours and internal abscesses7. Pashanabheda, shwadanshtra, varuna, kulattha and katakaphala-all equal in quantity are made into decoction, to this are added the paste of drugs of ushakadi gana and ghrita and medicated ghee prepared. This ghee consumed (daily) breaks ashmani (calculus) produced by vata8.Tarkari, varuna are madhura, ishat tikta and kaphavatanashaka9.The drugs of varunadi gana are used in kapha, meda, gulma agnimandya, adhyavata, shirahshula, and antarvidradhi10. Pashanabheda, varuna, shigru etc. drugs are used to make decoction and add drugs of ushakadi gana as prakshepa to make ghrit. Use of this ghrit destroys vatajanya ashmari suddenly11. The decoction of drugs of varunadi gana used in kapha, meda, gulma, shirahshula and antarvidradhi12. In the decoction of root bark of varuna adding kalka (paste) of varuna by using mild heat and decoction of root of shigru destroy the ashmari13.Bark of Sahijana and varuana take in equal amount to make decoction and add yavakshara as prakshepa. Use of this decoction destroys kaphashmari as thunder destroys the tree14.Take 2 tola bark of varuna and 32 tola of water to make decoction, remaining ¼ part filter and add yavakshara, sharkara etc. as prakshepa or in the decoction of varuna add 2 masha powder of bark of varuna and 2 tola guda, after taking this decoction ashmari and related pain subsides. Similarly by taking decoction of bark of sahijana with guda vatashmari destroyed15.
Varuna
Botanical Name-Crataeva nurvala Buch-Ham, Family- Capparidaceae.Three-leaved caper (Eng.)Erect or crooked trees up to 20 meters tall, branching high above the ground, moderate-sized deciduous tree.Leaves petiole with a distinct knob, consisting of glands leaflets 2-4 times as long as broad, top gradually acuminate with and acute tip, mid rib reddish tinged, across, nerves prominent beneath. Inflorescence terminal on leafy twigs, pedicels having their prominent scars on it. Petals clawed. Stamens on androphore and gynophore, stigma distinct, sessile. Berry covered with yellow grayish crust, puling off later, deep orange, seeds dorsally crusted. Plant flowers in February-April and Fruits in May-July. Plant is occurring in South-Asia and Indo-Malaysian Zone. Plant in commonly planted in Uttar Pradesh, central India. It is wild in dry deciduous forests. Important species are C. adansonii Dc. – Flowers and Fruits in April-June. Plant occurs in M.P. and Central India. Small tree plant C. unilocularis Buch-Ham. – Small tree with full foliage during anthes. Plant flowers and fruits in March-June. Plant occurs in dry deciduous forests in Central Provinces.All the three relevant species of crateva genus morphologically differ on the basis of characteristics of mainly flowers, fruits and leafs along with some other features of plant habit.
The bark contains tannin, saponin, flavonoids, glucosinolates and plant sterols including lupeol.Rasa- Tikta,Kashaya,Guna-Laghu,
ruksha, Virya–ushna, Vipaka-Katu, Doshkarms –Kaphavatashamaka. Varunadi, Vatashmarinashana, Kaphashmarinashana (Sushruta Samhita)
Therapeutic uses
The drug varuna is an effective diuretic and lithontriptic (ashmari bhedana) herbal agent, it is alterative, diuretic, anthelmintic, laxatives, demulcent, carminative and stomachic, obesity, calculi and urinary diseases. The bark is bitter, anti-periodic, tonic and demulcent and has a stimulating action on the liver. The root bark is rubefacient and counterirritant. The leaves have the properly of reddening and even blistering the skins. The bark of varuana is frequently given in the management of U.T.I. (urinary tract infection) renal calculus, renal colic, calculus, gravels, dysuria, etc. Its efficiency is as anti-septic.
Shigru
Botanical name – Moringa oleifera Lam., Family – Moringaceae.Fairly large tree, bark corky, wood soft, white spongy. Leaves 30-76 cm. long, three pinnate, petiole sheathing at base, pinnate 4-6 pairs, opposite the uppermost pair, foliate, hairy gland present between each pair of pinnae and pinnulae , ultimate leaflets opposite 0.85-1.7 cm. long, obovate or elliptic entire, membraneous, pale beneath. Flowers 2-5 cm. diam, strongly honey scented; sepals, reflexed linear lanceolate, petals 1.7-2.5 cm. linear spathulate, white with yellow dot near base, filament villous at base, ovary hairy. Capsule 23 x 50.8 x 1.3 – 1.7 cm. trigonous, linear peduncles longitudinally ribbed with slight constrictions between seeds. Seeds three cornered, winged, about 2 cm. long and corky testa, non-endospermic, having straight embryo, convex cotyledons, superior radicle and many leaved plumule.Root bark is Grayish brown reticulated marked with tumid projections of discontinuous transverse rows of transversely extended lenticles 2-8 mm. long. Dents may show tears of reddish of reddish gum. Slightly succulent, outer skin is corky and papery. Tissue inside is or rose.
Portion nearest to wood is whitish. Wood is very soft porous and yellow in colour. Plant flowers from January to March and Fruiting in April- June. Plant is indigenous in sub-Himalayan tract. It is commonly cultivated throughout the country. Plant is found in Assam, Gujarat and Uttar Pradesh. There are two kinds of shigru in classical texts of medicine on the basis of flower color viz. while and Red, which are bitter and sweet (katu-madhura) in tastes and they are specifically known as Katushigru and Madhushigru respectively.
Katushigru botanically identified as M. oleifera lam, us occurring almost throughout country and available commonly, but Madhushigru, botanically identified as M. concanensis with restricted distribution in Bangal, Sindha. Leaves bi-pinnate somewhat longer than those of M. oleifera lam, and flowers pinkish yellow in colour in case of M.concanensis Nimmo.Another kind of Shigru is Nila Shigru (blue variety) in texts of material medica (Nighantu).Root bark contains moringine alkaloids, Roots contain an antibiotic principle pterygospermin. Seeds yield fixed oil 36.6 % .Bark yields a gumresin.
Pressed juice of Pods contains: Ascorbic acid oxidase.Pods contain Globulin (N 15.6 Sulphur 1.58 %), Prolamin (N 14.02, Sulphur 1.43 %).The Pods are remarkably rich in free lencine. Rasa – Katu (kshariya), Tikta, Guna – Laghu, ruksha, tikshna, Virya – ushna, Vipaka- Katu,Doshkarma – Kaphavatashamaka. Svedopaga, Krimighna, Shirovirechanopaga, Katukaskandha, Haritakavarga (Charak Samhita), Varunadi, Sirovirechana (Sushruta Samhita).
Therapeutic Uses
The drug shigru is antihistaminic, abortifacient, anthelmintic antiseptic, aphrodisiac, astringent, cardiotonic, carminative, stomachic and tonic. It is used in general anasarca, cancerous growth, glandular disease, intermittent forever obesity, paralyses of different organs, rheumatism, splenic disordered and wounds. Pterygospermin exhibits high activity organs against gram positive and gram negative bacteria including mycobacterium tuberculosis, fungi
Urinary calculi consist of aggregates of crystals containing small amounts of proteins and glycoprotein.
Renal stones in which the crystalline component consist of calcium oxalate are the most common and stones containing calcium as oxalate, phosphate or both comprise about 80 % of the total. About 15 % contain magnesium ammonium phosphate and small numbers of pure cystine or uric acid stones are found. Rarely drugs may form stones e.g. indinavir, ephedrine.Urinary concretions vary greatly in size. There may be particles like sand any where in the urinary tract or large round stones in the bladder. Staghoren calculi fill the whole renal pelvis and branch into the calyces. Deposit of calcium may be present throughout the renal parenchyma, giving rise to nephrocalcinosis17.
Table 1
| The pods of Shigru contains | Leaves Analysis | ||
| Moisture | 86.9 | Moisture | 75 |
| Protein | 2.5 | Protein | 6.7 |
| Fat | 4.8 | Fat (ether ext.) | 1.7 |
| Mineral matter | 2 | Mineral matter | 2.3 |
| Calcium | 30 | Calcium | 440 |
| Phosphorous | 1.1 | Phosphorous | 70 |
| Iron | 5.3 mg. / 100 g. | Iron | 700 mg. / 100 g. |
| Copper | 3.1 ug. / g. | Copper | 1.1 ug. / g. |
| Iodine | 18 ug. / kg. | Iodine | 51 ug. / kg. |
| Oxalic acid | 0.01 | Carbohydrate | 13.4 |
| Carotene (as vitamin) | 184 I.U. | Carotene | Rich |
| Nicotinic acid | 0.2 mg. | Fiber | 0.9 |
| Ascorbic acid | 120 mg. / 100 g. | Ascorbic acid | Rich |
Table 2
| S.No. | Varuna | Shigru | Varuna- Shigru Kwatha | |
| 1. Rasa | Tikta, Kashaya, | Katu (Kshariya), Tikta | Katu, Tikta, Kashaya | |
| 2. Guna | Laghu, Ruksha | Laghu, Ruksh,Tikshna | Laghu, Ruksh,Tikshna | |
| 3. Virya | Ushna | Ushna | Ushna | |
| 4. Vipaka | Katu | Katu | Katu | |
| 5. Doshkarma | Kaphavatashamaka, | Kaphavatashamaka, | Kaphavatashamaka, | |
| Pithavardhana. | Pithavardhana. | Pithavardhana. | ||
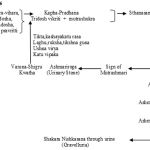 |
Figure 1:
|
Discussion
Concept of Varuna-Shigru Kwatha is seen first time in Yogaratnakar in Ashmarichikitsa. The description of varuna along with shigru for kwatha also given by other scholar likes Charaka, Sushruta, Chakradatta, Bhav Prakash, Bhaishajyaratnawali, etc.The main aim of Varuna-Shigru Kwatha is Ashmarinashana. Varuna is having Tikta, kashaya rasa, laghu, ruksha guna, ushna virya and katu vipaka. By this virtue it is kaphavatashamaka, Shigru is having katu, tikta rasa, laghu, ruksha, tiksna guna, ushna virya and katu vipaka, by this virtue it is Kaphavatashamaka.Dose of this kwatha is 50-100ml.
Refrences
- Charaka Samhita (C.Su.4/25)
- Sharangadhara Samhita (Sha.M.Kha.2/7)
- Charaka Samhita (C.Su.14/31)
- Charaka Samhita (C.Ci.3/267)
- Charaka Samhita (C.Ci.14/45)
- Charaka Samhita (C.Ci.26-67)
- Sushruta Samhita(S.Su.38/10)
- Sushruta Samhita(S.Ci.7/6)
- Ashtanga Hridaya(A.H.Su.6/97)
- Ashtanga Hridaya(A.H.Su.15/21)
- Ashtanga Hridaya (A.H.Ci.11/19)
- Sharangadhara Samhita (Sha.M.Kha.2/28)
- Bhava Prakash(B.P.Ashmari.37-65)
- Yogaratnakar Ashmarichikitsa
- Bhaishajya Ratnawali(B.R.Ashmari.36/6)
- Charaka Samhita (C.Ci.26/36)
- Davidson’s Principles and Practice of Medicine,632.







