Arikatla V. Rao*, Arshi Naqvi, Mohd. Shahnawaaz, Daya S. Seth and Peter E. Joseph
School of Chemical Sciences, Chemistry Department, St. John's College, Agra - 282 002 India.
Corresponding Author E-mail: rao_arikatla@yahoo.co.in
Abstract
The synthesis of thiosemicarbazides has been the area of extensive research since decades especially while investigating compounds to be potential pharmacological candidates. In this paper, we propose the synthesis of title compounds by the condensation of o-toluidine and p-toluidine malonamic acid hydrazides with substituted phenyl isothiocyanates under microwave irradiation. The synthesized compounds were subjected to antibacterial screenings.
Keywords
Synthesis; thiosemicarbazides; microwave irradiation; antibacterial screenings
Download this article as:| Copy the following to cite this article: Rao A. V, Naqvi A, Shahnawaaz M, Seth D. S, Joseph P. E. Greener Synthesis of Pharmacologically Important Thiosemicarbazides. Biomed Pharmacol J. 2009;2(1) |
| Copy the following to cite this URL: Rao A. V, Naqvi A, Shahnawaaz M, Seth D. S, Joseph P. E. Greener Synthesis of Pharmacologically Important Thiosemicarbazides. Biomed Pharmacol J. 2009;2(1). Available from: http://biomedpharmajournal.org/?p=704 |
Introduction
The synthesis of thiosemicarbazides has been the area of extensive research since decades especially while investigating compounds to be potential pharmacological candidates. Thiosemicarbazides have shown unique spectrum of anticonvulsant1, antifungal2, plant growth promoting3, antibacterial4, anti-tubercular5 properties. Microwave Assisted Organic Synthesis (MAOS) serve as one of the greener methodologies in organic synthesis. It has become increasingly important in performing chemical transformations in minutes instead of hours by conventional methods.
Under the framework of “MAOS” we propose to present a very simple, fast and ecofriendly procedure where the reaction of substituted isothiocyanate with substituted acid hydrazides leads for the synthesis of some thiosemicarbazides. The synthesized compounds were evaluated for anti bacterial activity against S. aureus and E. coli.
Experimental
Melting points were determined in open capillary tubes and are uncorrected. The purities of the compounds were checked on silica-gel-coated Al plates (Merck). 1H-NMR spectra was measured on Advance Bruker DRX-300 using solution in hexadeuterio dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) with trimethyl silane(TMS) as the internal standard , chemical shifts are given in δ (ppm) and protons signals are indicated as :s= singlet, d = doublet, t = triplet, m = multiplet. Elemental analysis was performed on Elementor Vario EL III at C.D.R.I., Lucknow.
IR spectra were recorded in KBr on a Perkin Elmer Spectrum RX-1 FT-IR spectrophotometer. Microwave irradiations were carried out in an IFB domestic microwave oven. All chemicals were of analytical grade.
General procedure
Method A(Heating). Substituted malonamic acid hydrazide(5mmol) and stirred solution of substituted phenyl isothiocyanates (5mmol) in ethanol (10 mL) was refluxed for 3 hrs, and then filtered to give the corresponding thiosemicarbazide which was recrystallized from ethanol6.
Method B(Microwave irradiation). Substituted malonamic acid hydrazide(5mmol), ethanol (5-8 drops) and substituted phenyl isothiocyanate (5mmol) were irradiated in microwave for 2-6 mins. Solid obtained was purified by recrystallization from hot ethanol.
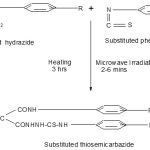 |
Scheme 1: |
R = 2-CH3 and 4-CH3
R1 = H, 4-Br, 4- OC2H5 and 4- CH3
Table 1: Thiosemicarbazides obtained by the condensation of N-(2-methyl) phenyl malonamic acid hydrazide with different phenyl isothiocyanates.
| S. No | R1 | Mol. Formula | M.P
(oC) |
% Yi
Visited 120 times, 1 visit(s) today
| |







