Ch. Narasimharaju BH1, G. DevalaRao2 and Rajendran Rukmani3
¹A.S.N.Pharmacy College, Burripalem Road, Tenali - 522 201 (Inda).
²KVSR Siddhartha College of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Vijayawada - 520 010 (India).
³Jaya College of Pharmacy, Thiruninravur - 602 024 (India).
Corresponding Author E-mail: bhchnraju@yahoo.com
Abstract
This paper describes about validated Reverse phase High Performance Liquid Chromatographic method for determination of Ezetimibe in bulk and pharmaceutical formulations has been developed. Chromatographic separation was carried out using a mobile phase of Potassium dihydrogen phosphate buffer (containing triethylamine) and acetonitrile (55:45v/v) on a C18 –ODS –Hypersil (5 µ, 250×4.6 mm) column in isocratic mode at a flow rate of 1.5ml/minute with UV detection at 234nm. Atorvastatin calcium was used as internal standard. The chromatographic method was linear over the concentration range of 50-250ìg/ml. The Limit of Detection and Limit of Quantitation were 0.828 and 2.5 µg/ml respectively. The mean percentage purity and recovery were found to be 101.22% and 100.36% respectively. Suitable method was developed to determine Ezetimibe in bulk and pharmaceutical formulations.
Keywords
RP -HPLC; Ezetimibe; Tablets
Download this article as:| Copy the following to cite this article: Narasimharaju B. C, DevalaRao G, Rukmani R.Reverse Phase High Performance Liquid Chromatographic Determination of Ezetimibe in Bulk and Pharmaceutical Formulations. Biomed. Pharmacol. J.2008;1(2) |
| Copy the following to cite this URL: Narasimharaju B. C, DevalaRao G, Rukmani R.Reverse Phase High Performance Liquid Chromatographic Determination of Ezetimibe in Bulk and Pharmaceutical Formulations. Biomed. Pharmacol. J.2008;1(2). Available from: http://biomedpharmajournal.org/?p=489 |
Introduction
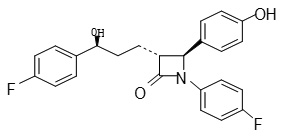
Ezetimibe is a new class of lipid lowering drug, which differs from other classes of cholesterol reducing compounds. It is chemically as (3R, 4S) – 1 – (4-Flourophenyl –3 Hydroxy propyl]-4-(Hydroxy phenyl-2-azetidinone.
James E.Patrick et al studied the Ezetimibe pharmacokinetics2. Literature survey reveals the availability of few analytical methods such as HPCL3-5 ,LC-MS6,derivative spectrophotometry7 and voltammetry8 for determination of Ezetimibe in pharmaceutical formulations .In the present investigation the authors propose a simple, sensitive and reproducible RP-HPLC method for the determination of Ezetimibe.
Expermental
Instrument
Shimadzu HPLC SPD-10ATVP, Japan equipped with UV visible detector Was used for HPLC analysis.
Chemicals and materials
Potassium dihydrogen phosphate, triethylamine and acetonitrile (HPLC grade) were procured from E.merck India, Limited. Water was purified by double distillation and filtered through 0.2μ pore sized membrane filter. Ezetimibe was obtained as a gift sample from Hetero Drug House Private Limited, Hyderabad, India. Two marketed brands of Ezetimibe were used for estimation.
The chromatographic separation was carried out in an isocratic mode utilizing Hypersil C18 column with dimensions (5μm, 250mmx4.6mm) as stationary phase and the mobile phase composed of buffer and acetonitrile in 55:45 ratios at a flow rate of 1.5ml/minute. The buffer was prepared using 1.3609g of potassium dihydrogen phosphate and 1.0ml of triethylamine Acetonitrile and water in 3:1 ratio was used as diluent.
Preparation of standard solutions
In Chromatographic determination, separate stock solutions of reference compound and internal standard were prepared by weighing the appropriate amount into volumetric flasks and made up to volume using the diluent. Specific volume of each solution relating to the required concentration were pipetted into volumetric flask and made to volume to obtain serial dilutions using the diluent.
Sample preparation
Twenty tablets of both brands were weighed and powdered in a mortar. In Chromatographic method, a quantity equivalent to 50 mg was weighed accurately and transferred into 100ml volumetric flask along with the internal standard. About 75 ml of diluent was added and sonicated for 30 minutes and made to volume. This solution was then filtered through membrane filter. First 10ml of solution was discarded and then diluted suitably to get a concentration of 100 μg/ml.
Method validation
Linearity
Calibration curve for chromatographic method was constructed by plotting ratio of peak areas (standard/internal standard) against concentration of solution. Figure 1 shows HPLC-UV chromatogram of Ezetimibe. Linear ranges and correlation coefficient9 Obtained for chromatographic method were depicted in table 1.
 |
Figure 1: CHROMATOGRAM of EZETIMIBE (100 mcg/ml).
|
Table 1: Analytical Performance Parameters of Ezetimibe
| PARAMETERS | EZETIMIBE |
RP-HPLC METHOD |
|
|
Linearity dynamic range (LDR;mg/ml) Correlation coefficient (r) Slope (m) Intercept (c)
|
50 – 250
0.9993
0.00862
0.05576
|
System suitability testing
System suitability for chromatographic method was determined by parameters like plate number; tailing factor, resolution factor and relative standard deviation. The data’s comply with ICH Standards10 and were presented in table 2.
Table 2: System Suitability Parameters (RP-HPLC).
|
Parameters
|
Ezetimibe |
Internal standard |
|
Retention Time (minutes)
Tailing Factor
Resolution Factor
Number Of Theoretical Plates
|
3.91
1.04
4.932
8298 |
5.64
1.01
4.932
7817 |
Tablet assay
Quantitative analysis was carried out in marketed brands of Ezetimibe, which are depicted in table 3.
Table 3: Quantification Parameters of Ezetimibe.
| Sample | Label claim | RP-HPLC method | ||
| Assay | %R.S.D | |||
| Tablet A
Tablet B |
10
10 |
101.22
103.30
|
0.1281 0.1307 |
|
Precision and accuracy
Precision was assessed by determining the relative standard deviation, Accuracy was determined by recovery studies, which was performed by spiking sample with known concentrations of standard. The datas were depicted in table 4.
Table 4: Recovery studies of Ezetimibe.
|
Sample concentration μg/ml |
Fortified concentration
μg/ml |
Percentage Recovery |
|
| Tablet A | Tablet B | ||
|
100
|
150 200 250 |
100.50 100.61 100.71
|
100.81 100.93 100.71
|
Results
The linearity was obeyed in the concentration range of 50-250 μg/ml in Chromatographic method. From the chromatogram, the retention times were found to be 3.91 minutes and 5.64 minutes for Ezetimibe and Atorvastatin respectively. The Limit of Detection and Limit of Quantitation were 0.828 and 2.5 μg/ml respectively. Quantitative estimation of the tablet showed average percentage purity of 101.22% with mean recovery of 100.36%. The system suitability parameters indicate that the developed method has acceptable accuracy and precision. In the above determined method, the relative standard deviation was below 1, which is a good index of accuracy and precision.
Conclusion
The developed method was simple, rapid, accurate, and reproducible was more suitable to determine Ezetimibe in bulk and pharmaceutical formulations.
Acknoledgement
The authors are grateful to m/s Hetero Drug House Private Limited, Hyderabad, for providing the authentic of Ezetimibe sample and Dr. Ceeal Analytical Lab, Chennai, for providing the facilities to carry out the present investigation.
References
- The Merck index, Thirteenth edition, Merck and co., Inc.U.S.A, 2002: pp 3949.
- James E. Patrick, Teddy Kosoglou, Kathe L. Stabber, Kevin B. Alton, Stephen E.Maxwell, Yali Zhu, Paul Statkevich, Robert Iannucci, Swapan Chowdhury, Melton Affrime, and Mitchell N. Cayen, Disposition of the Selective Cholesterol Absorption Inhibitor Ezetimibe in Healthy Male Subjects, Journal of Drug metabolism and Disposition,2002:30(4); 430-437.
- MuhammadAshfaq, IslamUllahkhan, SyedShanazQutab, SyedNaeemrazzaq, HPLC Determination of Ezetimibe and simvastatin in pharmaceutical Formulations,Chil .chem.soc, 52 no 3(2007).1220-1223.
- Carlucci, P.Mazzeco,L.Biordi, M.Bologna, J.Pharm.Biomed.Anal, 10 (9), 693 (1992).
- Ochiai, N.Uchiyama, K.Imagaki, S.Hata,T.Kamei.,J.Chromatogr.B.Biomed
- .Sci.Appl,.694(1),211(1997).
- Barrett,JHuclova.V.BorekDohalsky,B.Nemec,I.Jelinek,J.Pharm.Biomed.Anal,41(2), 517(2006).
- Wang,M.Asgharnejad ,J.Pharm.Biomed,Anal,21(6),1243(2000).
- Corah.S.AOzkan,Pharmazie,61(4),285(2006)..
- Frederick J Gravette’s, Lancy B and Wallnau, Essential of Statistics for the behavioral Sciences, 2nd Edition, West Publishing Company, 1995, PP2-4, 173-175.
- ICH Steering Committee, Validation of analytical procedures/methodology, ICH Harmonized Tripartite Guidelines, 1996.