Nour Athiroh Abdoes Sjakoer1* and Yudi Purnomo2
and Yudi Purnomo2
1Departement of Biology, Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences, Universitas Islam Malang, Malang, Indonesia
2Departement of Pharmacy, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Islam Malang, Malang, Indonesia
Corresponding Author E-mail: nour.athiroh@unisma.ac.id
DOI : https://dx.doi.org/10.13005/bpj/2562
Abstract
Hypertension is a degenerative disease that become health problem in the world. S. atropurpurea BI. Dans and D. petandra are herbs that showed anti-hypertension activity. However, the potency of their combination onimmune system in hypertension condition have not been explored completely. The study aim to examine effect of S. atropurpurea BI. Dans and D. petandra combination on Cluster of Differentiation 4 (CD4), Cluster of Differentiation 8(CD8), interleukin-10 (IL-10), and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF- α) level in hypertension rats. The rat was administrated orally with methanolic extract of S. atropurpurea BI. Dans and D. petandra (1:3) combination at dose of 50 mg/kgBW (P1), 100 mg/kgBW (P2) and 200 mg/kgBW (P3) for four weeks. Hypertension rats are induced with Deoxycorticosterone acetate (DOCA) and salt orally at the second weeks after herbs administration. Blood sample was collected from intra cardiac, furthermore, the level of IL-10 and TNF-α levels are examined using the Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) method, whereas CD4 and CD8 levels are examined using flow cytometri. The data was analyzed using ANOVA test continued with LSD test (p < 0,05). The treatment groups (PI, P2, and P3) showed an increase of CD4 levels more and less 3 times,10 times, and 8 times respectively; an increase of CD8 level about 2 times, 3 times, and 2 times respectively compare to hypertension group (p<0.05). However, IL-10 level were increased only by P3 group (p<0.05). Meanwhile, the combination of herbsdecreased TNF-α level approximately 50-60% for three doses used (p<0.05). Combination of methanolic extracts of S. atropurpurea BI. Dans and D. petandra increase CD4, CD8 and IL-10 level and decreased TNF-α level on hypertension rat.
Keywords
Cluster of Differentiation 4 (CD4); Cluster of Differentiation 8(CD8); D. petandra; Hypertension; interleukin-10 (IL-10); S. atropurpurea BI. Dans; Tumor Necrosis Factor-α (TNF- α)
Download this article as:| Copy the following to cite this article: Sjakoer N. A. A, Purnomo Y. The Effect of Tea Epiphyte (Scurrula atropurpurea BI. Dans) and Mango Epiphyte (Dendrophthoe petandra) Combination on CD4, CD8, IL-10, and TNF-α Levels in Hypertension Rats. Biomed Pharmacol J 2022;15(4). |
| Copy the following to cite this URL: Sjakoer N. A. A, Purnomo Y. The Effect of Tea Epiphyte (Scurrula atropurpurea BI. Dans) and Mango Epiphyte (Dendrophthoe petandra) Combination on CD4, CD8, IL-10, and TNF-α Levels in Hypertension Rats. Biomed Pharmacol J 2022;15(4). Available from: https://bit.ly/3u2xsKx |
Introduction
Hypertension is becoming a global health problem around the world. Hypertension is defined as a condition in which a person’s blood pressure is ≥ 140 mmHg (systolic) and/or ≥ 90 mmHg (diastolic) 1. Hypertension reduce quality of life and increase risk factors for cardiovascular disease, it is called a silent killer due to contribute mortality number at all age group 2,3. Based on survey, the prevalence of hypertension in Indonesia people over 18 years old is 33.4% in 2014-2015 and it will be increase each year 4.
Both of pharmacological and non-pharmacological therapy are performed to reduce mortality and morbidity number 5,6. The use of herbal medicine to treat hypertension has increased as a result of the “back to nature” trend. They are claimed to be safe, cheap and easy to obtain 7. Two of these are the herbal tea epiphyte (Scurrula atropurpurea BI. Dans) and the mango epiphyte (Dendrophthoe petandra). The S. atropurpurea BI Dans is popular as anti-cancer that contains flavonoid, fatty acids, xanthine, and avanol glycosides 8,9. In vitro studies showed they able to decrease the contractility of the rat tail arteries as a result of the endothelium’s function 10,11. Meanwhile, in vivo studies have indicated the ability of herbs to improve endothelial dysfunction through reducing of Malondialdehyde (MDA) levels and increasing of superoxide dismutase (SOD levels 11-12. Whereas D. Petandra contains anticancer substances also such as flavonoids, antioxidants, saponins, and polyphenols. The flavonoids and tannins in D. petandra are predicted to have antihypertensive properties through reducing oxidative stress. Combination methanolic extract of S. atropurpurea BI Dans and D. petandra are expected able to increase their activity and also reduce their toxicity 13.
The herbs contain many active compound are predicted to have some pharmacology effect. Beside as anti-hypertension, S. atropurpurea BI Dans and D. petandra are predicted have additional effect as anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory. Their activity support the immune system to prevent infection and reduce inflammation process which involved in degenerative diseases. Inflammation process related to immune response, cytokine pro inflammatory is needed to activate immunocompetent cells such as monocytes, macrophages, and lymphocytes. They stimulate antibody production is used to eradicate infection 14. However, the excessive of cytokine pro inflammatory including interleukins (IL) and tumor necrosis factor (TNF) exacerbate existing hypertension and induce an inflammatory process of the vascular endothelium that leads to high blood pressure 15. The high production of cytokines can cause abnormal development of endothelial and vascular smooth muscle cells, as well as an imbalance of endogenous vasodilators and vasoconstrictors 16.
Based on the explanation above, this study aim to evaluate the combination of S. atropurpurea BI Dans, and D. petandra extracts as immunomodulatory agents in animals model hypertension.
Material and Methods
Materials
The material used is simplicia of S. atropurpurea BI. Dans and D. petandra, anti CD4 and CD8 antibodies (Santacruz, USA), quantikine reagent (R&D System USA) with a minimum detection dose of 0.5-5.5 pg/ml and a minimum detection mean of 1.6 pg/ml ml, aquadest, phosphate buffered saline (PBS), methanol 90%, doxycorticosterone acetate (DOCA-salt), dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), and tween/polysorbate 80 (Sigma Aldrich, Darmstadt, Germany).
Methods
Extracts Preparation
The simplicia of S. atropurpurea BI. Dans and D. petandra were blended into powder. The powder weighed 100 grams and was then processed by the maceration method with 1 liter of 90% methanol for 24 hours at room temperature. The macerated material is then filtered through filter paper. At a temperature of 40oC, the supernatant was evaporated in a rotary evaporator. Methanol extract of S. atropurpurea BI. Dans and D. petandra can be stored until further examination.
Animal Preparation
In total, 75 male wistar rats (Rattus nivergicus) aged 2-3 months were employed in the study. The test animals were acclimatized for 5 days at the Animal House, Faculty of Dentistry, Brawijaya University Malang, which is sheltered from industrial emissions, motor vehicle fumes, and other pollutants and has a room temperature of 24oC and an air humidity of 50-60%. Feeding and drinking are performed (morning and evening). Following the acclimatization procedure, there is a 28-day maintenance period under the same conditions as the acclimatization period. The Health Research Ethics Commission, Faculty of Medicine, Islamic University of Malang (Ethical Clearance) Number: 006/LE.001/IV/03/2020 has given permission for these test animals to stay alive.
The animals were separated into five groups: a negative control group K(-) that received no treatment, a positive control group K(+) that received only DOCA-salt induction, and three treatment groups (P1, P2, and P3) that received DOCA-salt induction. They were given a different dose of S. atropurpurea BI. Dans and D. petandra methanolic extract.
Herbs Administration
. The administration is completed five times in one week. The combination dose of methanolic extracts of S. atropurpurea BI. Dans and D. petandra with a ratio of 3:1, the first dose (group P1) being 50 mg/Kg BW, the second dose (group P2) being 100 mg/KgBW, and the third dose (group P1) being 200 mg/KgBW.
Induction of animal Hypertension Mode
DOCA was given subcutaneously in the K(+) or hypertension group, P1, P2, and P3 groups for the last two weeks to establish a hypertensive rat model. DOCA is injected twice within a week. Along with the administration of DOCA, the giving of salt water was performed to the animal orally every day.
Sacrifice and measure biomarker
After the test animals had been treated for 28 days, sacrifice was conducted. Ketamine was used to induce sedative in the animal before sacrifice. The rats’ spleen and blood were removed for analysis of the levels of CD4, CD8, IL-10, and TNF-α. The immunohistochemistry technique was used to examine CD4 and CD8 level. Meanwhile, IL-10 and TNF-α levels were determined using the ELISA technique.
Data Analysis
A one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) test was used to analyze the data, followed by a post-hoc test if there were significant differences. The JAMOVI application version 1.1.9 is used for this data analysis
Results and Discussion
Effect of combination herbs on CD4 Levels
Figure 1 showed the combination extract of S. atropurpurea BI. Dans and D. petandra in PI, P2, and P3 groups increased CD4 levels about 3 times, 10 times, and 8 times respectively compared to the hypertension group or K(+) (p<0.05). The administration of herbs at P2 and P3 groups increased CD4 levels until they were not different compared to normal group or K(-) (p>0.05). The CD4 levels in hypertension group or K(+) decreased about 5 times fold compared to normal group or K(-) (p<0.05).
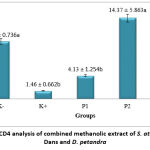 |
Figure 1: The CD4 analysis of combined methanolic extract of S. atropurpurea BI. Dans and D. petandra |
Hypertension induces an immune response, especially an inflammatory process with a reducing in CD4 levels. Furthermore, it decreased immune system and lost the activity to fight infection. A combined methanolic extract of S. atropurpurea BI. Dans and D. petandra contained alkaloids and flavonoids having immunomodulatory effect. They prevent a decrease of CD4 levels and also the inflammation, therefore it reduced the risk of infection and hypertension exacerbate 17,18. CD4 serves a critical role in immunity by stimulating the non-specific immune system such as phagocytes for chemotaxis and the process of phagocytosis of foreign substances. CD4 also plays a role in the humoral immune system by stimulating B cells (B lymphocytes) to regulate antibody production 19.
Effect of combination herbs on CD8 Levels
Figure 2 indicated the administration of S. atropurpurea BI. Dans and D. petandra in P1, P2 and P3 groups increased CD8 levels approximately 2 times, 3 times, and 2 times folds respectively compared to hypertension group or K(+) (p>0.05). CD8 levels in hypertension group was lower than normal group and treatment group (p>0.05).
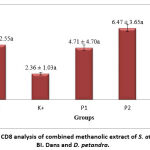 |
Figure 2: The CD8 analysis of combined methanolic extract of S. atropurpurea BI. Dans and D. petandra. |
An increase of CD8 level is aimed to keep the inflammatory process under control. If the CD8 count in a huge numbers, the immune system will overreact, as seen in autoimmune diseases 20. Hypertension causes an immune response, especially an inflammatory process with a decrease of CD8 level, therefore it affect immune system to fight infection. A combined methanolic extract of S. atropurpurea BI. Dans and D. petandra contains alkaloids and flavonoids that are immunomodulatory agent. Their activity to inhibit inflammation and tissue damage, meanwhile increasing CD8 levels, resulted the body’s resilience to infection 17. However, the excessive of CD8 count caused over reactivity of immune system and produces autoimmune diseases.
Effect of combination herbs on IL-10 Levels
Figure 3 indicated that there was an increase of IL-10 levels in the P3 groups about 100% compared to hypertension groups (p<0.05). Meanwhile, P1 and P2 group increased IL-10 levels not significant about 10% and 5% respectively compared to hypertension groups (p>0.05). IL-10 levels in hypertension group was higher 5% than normal group (p<0.05).
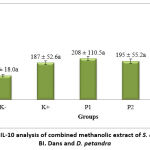 |
Figure 3: The IL-10 analysis of combined methanolic extract of S. atropurpurea BI. Dans and D. petandra |
Hypertension induces an inflammatory process with an increase of IL-10 levels as response to cell injury. Inflammation chronic caused endothelial disfunction and exacerbate hypertension. However, as compensation the body suppressed the inflammation condition by producing cytokine anti-inflammatory and antioxidant. IL-10 is an anti-inflammatory cytokine that plays a crucial role in preventing inflammatory and autoimmune pathologies 21. A combined methanolic extract of S. atropurpurea BI. Dans and D. petandra contained alkaloids and flavonoids having anti-inflammatory, they decrease inflammation and cells damage. An increase of anti-inflammatory cytokines is advantageous because it can prevent more endothelial cell damage caused by hypertension. Furthermore, it can prevent interference and further damage caused by hypertension. IL-10 is released to reduce inflammation and reduce the harmful symptoms that come from excessive of inflammation 22.
Effect of combination herbs on TNF–α Levels
Figure 4 showed that the oral administration of herbs combination in P1, P2 and P3 groups were able to decrease TNF-α levels about 50%, 50% and 60% (p<0.05) respectively compared to hypertension group. TNF-α levels in hypertension group increased 4 times folds compared to normal group and treatment group (p<0.05).
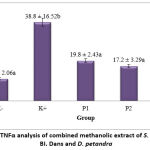 |
Figure 4: TNFα analysis of combined methanolic extract of S. atropurpurea BI. Dans and D. petandra |
Hypertension induces an immune response, especially an inflammatory process with an increase of TNF-α levels. Therefore, it increased endothelial disfunction and exacerbate hypertension. Endothelial injury can cause hypertension because the equilibrium of vasoconstriction and vasodilation is disrupted 23. This condition stimulated an inflammatory response and resulting in an increase of pro-inflammatory cytokines like TNF-α. Furthermore, hypertension condition resulted endothelial cell injury or damage, which can increase the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines 24. The combined methanolic extract of S. atropurpurea BI. Dans and D. petandra reduced TNF-α levels due to active components in herbs that have anti-hypertensive, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties, such as flavonoids 17. The decrease of blood pressure reduces cell damage and also the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Meanwhile, anti-inflammatory substances decreased cell damage, which reduces the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Antioxidant agent eradicated pro-inflammatory cytokines which having free radicals activity. Their activity caused the level of TNF-α could be decreased 24.
Conclusion
The combination of methanolic extract of S. atropurpurea BI. Dans and D.petandra in hypertensive rats (DOCA-Salt) has an effect on increasing levels of CD4, CD8, IL-10 which play a role in fighting infection and acting as an anti-inflammatory, while TNF will show a decrease in levels, which are proinflammatory cytokines.
Conflict of Interest
All authors declare there is no conflict of interest in this manuscript.
Reference
- Michael, Natalia D, Margaretta S.L, Putra W.D.R. Tata Laksana Terkini pada Hipertensi. J Kedokt Meditek,2014; 20(52):36-41.
- World Health Organization. A global brief on hypertension: silent killer, global public health crisis: World Health Day (No. WHO/DCO/WHD/2013.2). 2013
CrossRef - Barron S, Balanda K, Hughes J, Fahy L. National and subnational hypertension prevalence estimates for the Republic of Ireland : better outcome and risk factor data are needed to produce better prevalence estimates. BMC Public Health,2014;14(1):1–10.
CrossRef - Peltzer K, and Pengpid, S. The prevalence and social determinants of hypertension among adults in Indonesia: a cross-sectional population-based national survey. International journal of hypertension, 2018; 5610725.
CrossRef - Abegaz T.M, Tefera Y.G, Befekadu T. Target Organ Damage and the Long Term Effect of Nonadherence to Clinical Practice Guidelines in Patients with Hypertension: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Int. J. Hypertens, 2017; 2637051. doi: 10.1155/2017/2637051
CrossRef - Shaito A, Thuan D.T.B, Phu H.T, Nguyen T.H.D, Hasan H, Halabi S, et al. Herbal medicine for cardiovascular diseases: efficacy, mechanisms, and safety. Frontiers in pharmacology, 2020; 11:
CrossRef - Rani I, Pradono D.I, Darusman L. Mikroenkapsulasi ekstrak formula pegagan kumis kucing sambiloto sebagai inhibitor angiotensin I converting enzyme secara in vitro. Jurnal Agribisnis dan Pengembangan Wilayah, 2011; 3(1):11-24.
- Athiroh N, Permatasari N. Mekanisme kerja benalu the pada pembuluh darah. Jurnal kedokteran Brawijaya,2012; 27(1):1-7.
CrossRef - Maheshwari, H. Pemanfaatan Obat Alami: Potensi Dan Prospek Pengembangannya. IPB. Bogor. 2002.
- Athiroh N, Widodo MA, dan Widjajanto E. Efek Scurrulao ortiana (Benalu Teh) dan Macrosolen Vaskular javanus (Benalu Jambu Mawar) terhadap Kontraktilitas Pembuluh Darah Arteri Ekor Tikus [Tesis]. Universitas Brawijaya. Malang; 1998: p. 6,10,
- Athiroh, N. Kontraktilitas Pembuluh Darah Arteri Ekor Tikus Terpisah Dengan atau Tanpa Endotel Setelah Pemberian Esktrak Scurrulao ortiana (Benalu Teh). Jurnal Berkala Hayati EdisiKhusus, 2009; 3(4): 31-34
- Athiroh N, Sulistryowati, E. Scurrula atropurpurea increase nitric oxide and decrease malondialdehyde in hypertensiverats. Universamedicina, 2013; 32(1): 44-50.
- Aini S.Q, AthirohA.S, Mubarakati N.J. Kadar Superoksida Dismutase (SOD) pada Paru-paru Tikus Hipertensi DOCA-Garam yang Dipapar Ekstrak Metanolik Benalu Tehdan Benalu Mangga. metamorfosa:Journal of Biological Sciences, 2021; 8(2):291-297.
CrossRef - Irawati L, Acang N, Irawati N. Ekspresi Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alfa (TNF-α) dan Interleukin-10 (IL-10) pada Infeksi Malaria Falciparum. Majalah KedokteranAndalas, 2015; 32(1): 16-28.
- Ascherl G, Hohenadl C, Schatz O, ShumayE, Bogner J, Eckhart L, et al. Infection with human immunodeficiency virus-1 increases expression of vascular endothelial cell growth factor in T cells: implication for acquired immunodeficiency syndrome associated vasculopathy Blood, 1999; 93(12):4232-424
CrossRef - Groth A, Vrugt B, Brock M, Speich R, Ulrich S, Huber LC. Inflammatory cytokines in pulmonary Respir Res., 2014;15(1):1-10.
CrossRef - Sholikhah AR, Rahayuningsih HM. Pengaruh Ekstrak Lompong (Colocasiaesculenta L. Schoot) 30 Menit Pengukusan Terhadap Aktivitas Fagositosis dan Kadar NO (Nitrit Oksida) MencitBalb/c Sebelum dan Sesudah Terinfeksi Listeria monocytogenes [Disertasi]: Diponegoro University; 2015
CrossRef - Mwanje AK, Ejoku J, Ssemogerere L, Lubulwa C, Namata C, Kwizera A, et al. Association between CD4 T cell counts and the immune status among adult critically ill HIV-negative patients in intensive care units in Uganda. AAS open research 2019; 2(2): 31517248.
CrossRef - Hana N. Formulasi Table Hisap Ekstrak Etanol Gambir (Uncaria gambir roxb) dengan Variasi Konsentrasi Polyvinyl Pyrrolidone (PVP) Sebagai Pengikat dan Pengaruhnya Terhadap Kadar CD4 dalam Darah [Skripsi]:Universitas Islam NegeriSyarifHidayatullah Jakarta;
- Deng Q, LuoY, Chang C, Wu H, Ding Y, Xiao R. The emerging epigenetic role of CD8+ T cells in autoimmune diseases: a systematic review. Frontiers in immunology 2019; 10:
CrossRef - Iyer SS, Cheng G. Role of interleukin 10 transcriptional regulation in inflammation and autoimmune disease. Critical Reviews™ in Immunology, 2012; 32(1).
CrossRef - Couper KN, Blount DG and Riley EM. IL-10: The Master Regulator of Immunity to Infection. The Journal of Immunology 2008; 180: 5771-5777.
CrossRef - Darwin E, Elfi E, Elfira D. Endotel: Fungsi dan disfungsi. Padang : Andalas University Press; 2018
- Aisah S, Djati S, Khotimah H. Pengaruh Polifenol The Hijau Terhadap Produksi TnNF-A (Tumour Necrosis Factor-A) Pada Kultur Sel Trofoblas Manusia Yang Dipapar Glukosa Tinggi 33 Mm. Farmasains: Jurnal Farmasi dan Ilmu Kesehatan, 2010; 1(1).
CrossRef








