Swapna R Nayaka1, Sabari Anand J V2, Shaik Mabu Shareef3 and Usha N S1*
1Department of Pharmacology, MVJ Medical College and Research Hospital, Hoskote - 562114, India
2Department of Pharmacology, MGMC, and RI, Mahatma Gandhi Medical College and Research Institute, Pondicherry, India.
3Department of Pharmacology, Kurnool Medical College, Kurnool - 518002, Andhra Pradesh, India.
Corresponding Author E-mail: drusha26@gmail.comDOI : https://dx.doi.org/10.13005/bpj/2069
Abstract
Seaweeds (Marine macroalgae) area large group of marine organisms containing important phytochemical constituents with various biologicalactivities .They are potentially prolific sources of highly bioactivese condary metabolites, which manifest many of the rapeutic effects like anti-cancer, anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory and anti-diabetic activities. Seaweeds are used by many Asian cultures fortraditional medicine preparations. The Caulerpapeltata was collected from Rameshwaram coastal area it was shadedried, madein to powder using standardized procedure to get Caulerpapeltata Methanolic Extract (CPME). The phytochemicals and Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS) analysis was done on prepared CPME for identifying the bioactive compounds Phytochemical in vestigation suggests that the Caulerpapeltata exhibited the presence of phytochemicals like Alkaloids, Carbohydrates, Phytosterols, Saponins and Diterpenes,which may contribute to its biological activities. GC-MS analysis showed 28 variety of compounds,among which Dibutylphthalate, n-hexadecanoic acid, and1,2–Benzenedic arboxylic acid was found in high percentage. The phytochemical studies and the compounds available in GC–MS showed that the Caulerpapeltata contain important bio active compounds,which may have anti-microbial,anti-fungal and anti-canceractivity. Further research is needed for finding its use in development of new pharmaceutical agent and its safe consumption by human for various health benefits.
Keywords
CPME; Caulerpapeltata; GC-Msanalysis; Phytochemicals
Download this article as:| Copy the following to cite this article: Nayaka S. R, Anand J. V. S, Shareef S. M, Usha N. S. Gas Chromatography – Mass Spectroscopy [ Gc-Ms ] Analysis and Phytochemical Screening for Bioactive Compounds in Caulerpapeltata(Greenalga). Biomed Pharmacol J 2020;13(4). |
| Copy the following to cite this URL: Nayaka S. R, Anand J. V. S, Shareef S. M, Usha N. S. Gas Chromatography – Mass Spectroscopy [ Gc-Ms ] Analysis and Phytochemical Screening for Bioactive Compounds in Caulerpapeltata(Greenalga). Biomed Pharmacol J 2020;13(4).Available from: https://bit.ly/3m7CMqs |
Introduction
Plant -derived compounds are fascinating the world due to their multifaceted therapeutic use in modern medicine. Medicinal plantsare abundant bio-resource of drugs for traditional system of medicine,nutraceuticals ,food supplements, folk medicines,pharmaceutical in termediates and chemical entities for developing synthetic drugs1.
Sea weed sor marine macroalgaea replants and ecologically, commercially valua bleliving marine resources that belong to the primitive groups of non-flowering plants without trueroot, stemand leaves i n the division Thallophyta of Plant kingdom.Marine macro algae are classified into four groups based on pigments, stored food materials, morphological and anatomical characters into Chlorophyta (Green seaweeds), Phaeophyta (Brown seaweeds), Rhodophyta (Redseaweeds) and Cyanophyta (Bluegreenalgae)2. Seaweeds obtained from coastal region are the potential marine resource for many biochemical compounds.Pharmaceutical importance of seaweeds globally has led to ample research to extract out bio active compounds from algae. Marine habitat is an abundant resource of functional materials such as poly unsaturated fatty acids, poly saccha rides,essential minerals and vitamins, antioxidants, enzymes and bio active peptides3.
The nutritional value of a food depends on its chemical composition such as carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, sugars and also the minerals present in them. Sea weeds are the rich source of bio active compounds like carotenoids, dietary fiber, protein,essential fatty acids, vitamins and mineral4 and they contain biologically active substances such as lipids, proteins, poly sacch a rides and poly phenol5. The bio chemical composition of sea weeds differs, which are affected by in flow of land sources, geographic areas as on of they ear and temperature of water6
Recently, the importance of sea weeds as a source of novel bio active sub stances is growing rapidly and researchers have revealed that their compound sex hibit various biological activities due to the secondary meta bolites7. The bio active compound sex tracted from different Marine algae have antioxidant ,antiviral ,anti fungal and anti microbial activities8.
Caulerpapeltata is marine green algae with small fleshy‘ umbrellas’ is sometimes seen on our southern shores growing on coral rubble, near reefs. The species shave several benefits for which it is consumed as food and also as medicine for its anti fungal properties & its potential to reduce blood pressure.Although,there are no comprehensive studies regarding the active components in this seaweed. Hence, the current research work has focused on the phyto chemical profiling of Caulerpapeltata and the active biochemical compounds were further identified using gas chromato graphic mass spectrometry analysis.
Materials and Methods
Collection of Seaweed
Caulerpapeltata was collected from the vedalaicoastal area of Rameshwaram, TamilNadu, India and Marine Biologist helped in identifying the sample. The herbarium of the Caulerpapeltata was prepared and stored.
Preparation of seaweed Material
After collection of the seaweed it was washed many times to remove epiphytes, sand particles, other species parts, etc. The collected sample was soaked in distilled water twice. After thorough washing, seaweed sample was shade dried, till it becomes moisture free.
Preparation of extracts
A dried sample of seaweed was ground into coarse powder in a mechanical grinder. The sample was subjected to maceration at 24- 25°C in95% methanol for about 72 hours. The methanolic extract was derived after the process of distillation, evaporation, and drying it under reduced pressure9.
Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectroscopy analysis
GC-MS analysis performed by using a Shimadzu QPQP-2010 Plus with Thermal Desorption System TD20.
Derivatization of plant extracts for GC-MS: In the ratio of 1:4, water and ethyl acetate was added to the separating funnel containing concentrated sample. Small amount of concentrated sample was taken in a separating funnel and shaken by adding in 1:4 ratio. The upper layer was collected and concentrated to 1.5 mlin therotary evaporator, which is taken in funnel to add 100µl N,O-Bis(trimethylsilyl) tri fluoro acetamide and trimethyl chlorosilane(BSTFA+TMCS) & 20µl of Pyridine and heat it at 60°Cf or half an hour. To this sample Aceto nitrile was added & filtered in to aconical flask to which 50µl BSTFA+TMCS was added and heated again at 60°C in a water bath for 30 minutes. The CPME was filtered usin g0. 45µ membrane filter to avial 10.
Identi fication of phyto constituents
The inter pretation of Mass-Spectrum of GC-MS of the unknown compound was compared with the known components using database stored in National Institute Standard and Technology (NIST).
Qualitative analysis of phyto chemical substance The sample was subjected to phyto chemical analysis for detection of alkaloids, carbohydrates, glycosides, saponins, phytosterols, phenols, tannins, flavonoids, diterpenes, proteins & amino acid using the standard qualitative procedures 11 -13.
Results and Discussion:
The extract wastested for various phyto chemicals & constituents like alkaloids, saponins, phytosterols, diterpenes & carbohydrates were recorded in C.peltata are shown in the Table No.1.
Table 1: Phyto chemicals presenting C.peltata methanolic extract.
| Phytochemicals | Chemicalanalysis&results |
| Alkaloids | Wagner’stest++, Hager’stest++
Dragendroff’stest++ |
| Saponins | Frothtest++, Foamtest++ |
| Phytosterols | LiebermannBurchard’stest++ |
| Diterpenes | Copperacetatetest++ |
| Carbohydrates | Molisch’stest++, Benedict’stest++
Fehling’stest++ |
Alkaloids in seaweeds have anti microbial, anti diarrheal & anthelminticaction3. In present study Caulerpapeltata methanolic extract contains alkaloids, which suggests that it can be used as medicinal drug.
Saponinsare integral component of Chinese medicine because it has discrete properties responsible for most of the biological actions. Hence, seaweeds use dinhyper cholesterolemia, hyperglycemia, to reduce weight & as antioxidant, anticancer, anti-inflammatory agents14. Our study confirms presence of Saponins in methanol extract of C.peltata, suggesting that its benefit in suppressing infections& inflammation caused due to bacteria & fungi.
The extract of C. peltata, can be used as antimicrobial & anti diarrhoeal agents as it consists of both phytosterols & diterpenes3. As Steroids have been reported to have anti bacterial properties 15.
Bio active compound sextensively researched in carbohydrate are sulfated polysaccha rides which possess good antibacterial, anti-viral activity 16. In our study C.peltata extract tested positive for carbohydrates suggesting that it can be used in medical field as anti bacterial & anti viral agents.The algaldietary fiber consists soluble poly saccharides having salient action s such as antioxidant, anticoagulant, anti mutagenic and anti tumour effect and have an key role in the modification of lipid metabolism in human body 17.
The results observed by Raja sulochana Petal, Venkatesh R. Petal, Jayasree NB Petal, on phyto chemical compounds 18-20 help our study on the usefulness of marine algae in traditional medicine and added anoteonthephy to chemical history.Due the presence of phyto constituents in the seaweeds, they are beneficial in obtaining drugs for treating various ailments in humans. The sephyto constituents possess anti bacterial 21, antiviral 22,anti fungal 23,anticoagulant,anti-tumor 24 and anti-inflam matory activities 25.
GC-MS analysis was conducted in crude extract of Caulerpapeltata.The current study 28 different biochemical compounds have been identified from methanolic extract of the algae Caulerpapeltata.The compounds exhibited a wide range in their nature. Largest peak area was observed for the compound Dibutyl phthalate & other phyto chemicals liken-hexadecanoic acid&1,2-Benzene dicarboxylic acid also have alargearea.The compound with highest molecular weight was Hexacosyl penta fluoropro pionate (Figure No.1 & table No.2).Major phyto chemical’s with their chemical structures mentioned in table 3.
The most abundant phyto compounds,Dibutylphth alateactsas anti metabolic agent 26,n-hexadecanoic acid has various bio logical activities like antioxidant, hypolipidaemic, nematocide, lubricant & haemolytic inhibitor 27,where as 1,2-Benzene dicarboxylic acid has anti microbial & anti fouling activity 28.Hence C.peltata should be extensively studieds otat it can be used in pharmaceutical industry for their medicinal value.
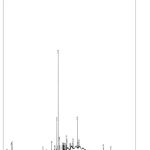 |
Figure 1: Chromatogram analysis of C.peltata |
Table 2: Phyto components in methanolic extract of Caulerpapeltata.
| Sl.No. | ReactionTime | Area% | Mol.weight | Compoundname | MolecularFormula |
| 1 | 7.163 | 1.33 | 115 | Acetamide,N,N-diethyl- | C6H13NO |
| 2 | 7.382 | 1.57 | 87 | Acetamide,N-Ethyl- | C4H9NO |
| 3 | 13.563 | 0.58 | 204 | Caryophyllene | C15H24 |
| 4 | 14.543 | 0.67 | 206 | Phenol,3,5-bis(1,1dimethylethyl)- | C14H22O |
| 5 | 15.533 | 2.52 | 222 | DiethylPhthalate | C12H14O4 |
| 6 | 16.482 | 0.48 | 226 | 8-Pentadecanone | C15H30O |
| 7 | 17.444 | 0.78 | 228 | Tetradecanoicacid | C14H28O2 |
| 8 | 17.819 | 1.23 | 238 | 1-Heptadecene | C17H34 |
| 9 | 18.278 | 0.91 | 278 | Neophytadiene | C20H38 |
| 10 | 18.542 | 0.62 | 278 | 1,2-benzenedicarboxylicacid,bis(2-methylp | C16H22O4 |
| 11 | 18.666 | 1.33 | 226 | 8-Pentadecanone | C15H30O |
| 12 | 19.175 | 2.73 | 270 | Hexadecanoic acid, methylester | C17H34O2 |
| 13 | 19.519 | 42.02 | 278 | Dibutylphthalate | C16H22O4 |
| 14 | 19.552 | 17.24 | 256 | n-Hexadecanoic acid | C16H32O2 |
| 15 | 19.865 | 1.65 | 266 | 1-Nonadecene | C19H38 |
| 16 | 19.986 | 0.84 | 340 | Eicosylacetate | C22H44O2 |
| 17 | 20.646 | 0.58 | 282 | 10-Nonadecanone | C19H38O |
| 18 | 20.813 | 1.33 | 268 | Oxirane,hexadecyl- | C18H36O |
| 19 | 20.872 | 0.41 | 296 | MethylDihydromalValate | C19H36O2 |
| 20 | 21.225 | 0.96 | 282 | Heptadecene-(8)-CarbonicAcid-(1) | C18H34O2 |
| 21 | 21.438 | 3.36 | 284 | Octadecanoicacid | C18H34O2 |
| 22 | 21.733 | 1.49 | 410 | Octacosanol | C28H58O |
| 23 | 21.843 | 1.16 | 340 | Eicosylacetate | C22H44O2 |
| 24 | 23.446 | 1.00 | 354 | n-Tetracosanol-1 | C24H50O |
| 25 | 24.562 | 10.22 | 390 | 1,2-Benzenedicarboxylicacid | C24H38O4 |
| 26 | 25.030 | 0.51 | 396 | 1-Heptacosanol | C27H56O |
| 27 | 27.861 | 0.92 | 528 | Hexacosylpentafluoropropionate | C29H53F5O2 |
| 28 | 31.520 | 1.55 | 386 | Cholesterol | C27H460 |
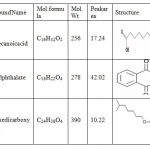 |
Table 3: Major phytochemical compounds in the methanolic extract of Caulerpapeltata & their chemical structure. |
Conclusion
The current study confirmed 28 distinct phytochemical substances present in the extract of Caulerpapeltata which could be the bio active constituents. ThealgaC.peltata are valuable reservoir of bio active compounds of medicinal interest which needs detailed studies so that it may beusedindrug for mulation by the pharmaceutical industries.
Acknowledgment
We acknowledge Dr S Bragdeeswaran, Associate Professor CAS in Marine biology, Annamalai University, who really gave invaluable support & contribution in the study.
Conflict of Interest
Authors declare there is no conflict of interest
Funding Source
There is no funding source
References
- Ncube NS,Afolayan AJ,OkohAI. Assessment techniques of antimicrobial properties of natural compounds of plant origin: current methods and future trends .J.Biotechnol .7(12):1797-1806. (2008)
CrossRef - RajakumarR and SinghAPY .Bio chemical investigation and GC-MS analysis of Gracilariaedulis. World JPharmRes. 6(7):1812-1820. (2017)
CrossRef - TiwariP, KumarB, KaurM, Petal.,Phyto chemical screening and Extraction: AReview. International epharmaceutic asciencia.1(1):98-106.(2011)
- BhaskarN & MiyashitaK. Lipid composition of Padinate tratomatica (Dictyotales, Phaeophyta), brown seaweed of the west coast of India. Fish.52(5):263-268. (2005)
- Chandini, SK, Ganesan, P & Bhaskar, N. Invitro activities of three selected brown seaweeds of India. Food Chem.107:707-713. (2008)
CrossRef - Present and future Needs for Alga and Algal products. Hydrobiologia. 260(1):15-23. (1993)
CrossRef - Kim,SK, WijesekaraI. Development and biological activities of marine derived bioactive peptides: Areview. JFunct Foods.2:1-9. (2010)
CrossRef - Chew,YL, LimYY, OmarM & KhooKS. Anti oxidant activity of three edible seaweeds from two areas in South East Asia. LWT. 41(6):1067-1072. (2008)
CrossRef - VasudevaraoB, Sravanthi DJ. GC/MS analysis and In-vitro Antioxidant activity of methanol extract of Ulothrixflacca and its main constituent Dimethyl Sulfone. IOSRJ Pharm Biol Sci.12(1):93-104. (2017)
CrossRef - Aneesh TP, ElizabethT, DellaGT & AnandanR. GC-MS analysis of Phyto chemical compounds presentin the Rhizomes of Nervilia aragoana GAUD. 6(3):68-74. (2013)
- Roopa shree TS, Dang R, Rani S R H & Narendra C. Anti bacterial activity of anti-psoriaticherbs : Cassiatora, Momordica charantia and Calendula of ficinalis. J.Appl. Res. Nat. Prod.1(3):20-28. (2008)
- Obasi NL, Egbuonu ACC, Ukoha PO & EjikemePM. Comparative phyto chemical and antimicrobial screening of some solven text racts of Samanea samanpods. J . PureAppl. Chem.4(9):206-212. (2010)
- Audu SA, Mohammed I, Kaita H A . Phyto chemical screening of the leaves of Lophiral anceolata (Ochanaceae). 4(4):75-79. (2007)
- RajA R, Mala K & Prakasam A .Phyto chemical analysis of marine macroalga Cauler para cemosa (J . agardh)[Chlorophyta– Caulerpales] from Tirunelveli district, Tamilnadu, India. 4(8):3055-3067. (2015)
- Epand R F , Savage P B, Epand R M. Bacterial lipid composition and anti microbial efficacy of cationic steroid compounds (Ceragenins). Biochim BiophysActa. 1768(10):2500-2509. (2007)
CrossRef - Gupta S& Ghannam, AN. Recent developments in the application of sea weeds orseaweed extract sasame ans for enhancing the safety and quality attributes of foods. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol.12(4):600-609. (2011)
CrossRef - Kolanji nathan,K, Ganesh P & Saranraj P. Pharmacological Importance of Seaweeds :A Review. Fish & Marine Sci.6(1):01-15. (2014)
- Raja sulochana P, Dhamotharan R, Krishna moorthyP . Primary Phyto chemical Analysis of Kappa phycus Sp. 5(2):91-96. (2009)
- Shanthi S ,Rajapandian petal,. Preliminary Study on Anti xantho monas Activity, Phyto chemical analysis ,and Characterization of antimicrobial compounds from Kappa phycusalvarezii. Asian JPharm Clin Res.4(3):46-51. (2011)
- Jaya sree N B,Aneesh T P, Prabhakar V and Anandan R.GC-MS, HPLC and A ASanalysis of Fatty Acids,Amino Acids and Minerals in Red Algae Amphiroaanceps. 4(1):187-190. (2012)
- Richards J, Kern E, Glasgow Letal ,Antiviral Activity of Extracts from Marine Algae. Antimicrob Agents and Chemother. 14(1):24-30. (1978)
- Oumas kour K, Boujaber N, Etahiri S and Assobhei O. Screening of antibacterial and antifungal activities ingreen and brown algae from the coast of Sidi Bouzid (El Jadida, Morocco).J.Biotechnol. 11(104):16831-16837. (2012)
- Athukorala, Y, Lee K, Kim Sand Jeon. Anticoagulant activity of marin egreen and brown algae collected from JejuIsland in Korea. 98(9):1711-1716.(2007)
CrossRef - Abirami, R G, Kowsalya S. Anticancer Activity of Methanolic and Aqueous Extract of Ulva Fasciatain albinomice. 4(2):681-684. (2012)
- Boonchum W, Peerapornpisa lY, Kanjanapothi Detal,. Antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties of various seaweeds from the Gulf of Thailand. J. Agric. Biol. 13:100-104. (2011)
- Roy R N, Laskar S, Sen S K. Dibutylphthalate, the bioactive compound produced by Streptomy cesalbido flavus 321.2.161(2):121-126. (2006)
CrossRef - Krishna moorthy K, Subramaniam P. Phytochemical profiling of Leaf, Stemand Tuber parts of Solena amplexicaulis (Lam.) Gandhi using GC-MS .2:1-13. (2014)
CrossRef - Maruthupandian A, Mohan V R. GC-MS analysis of some bioactive constituents of Pterocarpusmarsupium Roxb .J. ChemtechRes. 3(3):1652-1657. (2011)







