Padmaja Priyadarshini Kar1, Bandana Rath1, Y. Roja Ramani2 and C. S. Maharana1
1Department of Pharmacology, MKCG Medical College, Berhampur, Odisha.
2Department of Pharmacology, SLN Medical College, Koraput, Odisha.
Corresponding Author E-mail: drbandana.rath@gmail.com
DOI : https://dx.doi.org/10.13005/bpj/1635
Abstract
Cyclophosphamide (CP), the most commonly used anti-neoplastic agent causes immunosuppression and toxic effects on various organs that are the limiting factors of cancer treatment. It can be hypothesized that addition of new immunopotentiating agents with detoxification properties would have beneficial role in cancer therapy. Many researchers have proved that, if certain plant products are combined with cancer chemotherapeutic agents, reduce toxicities and improve tumour response. In Ayurveda, Gymnema sylvestre is commonly used for diabetes, obesity and asthma. Also it possesses anti-inflammatory, astringent and digestive properties. Reports on the immunostimulatory activity of Gymnema sylvestre leaves are available from some in vitro and in vivo experiments. With this background the present study was undertaken to evaluate the potential beneficial role of hydro-alcoholic extract of Gymnema sylvestre leaves (GSE) on cyclophosphamide induced immunnosupression in rats. In this experiment, five groups (n=6 in each) of wistar albino rats were randomly divided to receive drugs and vehicle orally for 21 days. Gr I and II received vehicle. Gr III, IV and V were administered with Levamisole 50 mg/kg, GSE 25mg/kg and GSE 50 mg/kg respectively. Except Gr I rats, all rats were injected intraperitoneally with Cyclophosphamide (100mg/kg) on day 9th and 16th of drug treatment. The effects on various organ weights, rise in Haemagglutination titre to Sheep RBC Antigen, delayed type of hypersensitivity (DTH) response to Sheep RBC, percentage of neutrophil adhesion to nylon fibre and phagocytic index from carbon clearance test were evaluated. Humoral and cellular immunity were measured from HA titre and DTH response respectively. It has been observed that, GSE 50 mg/kg significantly increased the antibody titre, percentage neutrophil adhesion and phagocytic index in CP induced immunosuppressed rats. It also restored the CP induced changes in organ weights and the DTH response at 24 and 48 hours of antigen challenge. But these effects were not comparable to that of Levamisole. Our study shows that Gymnema sylvestre reduced the CP induced immunotoxicities and therefore, it could be a safe supplement to cyclophosphamide chemotherapy.
Keywords
Albino Rats; Cyclophosphamide; Gymnem Sylvestre; Immunomodulation
Download this article as:| Copy the following to cite this article: Kar P. P, Rath B, Ramani Y. R, Maharana C. S. Amelioration of Cyclophosphamide Induced Immunosupression by the Hydro-Alcoholic Extract of Gymnema Sylvestre Leaves in Albino Rats. Biomed Pharmacol J 2019;12(1). |
| Copy the following to cite this URL: Kar P. P, Rath B, Ramani Y. R, Maharana C. S. Amelioration of Cyclophosphamide Induced Immunosupression by the Hydro-Alcoholic Extract of Gymnema Sylvestre Leaves in Albino Rats. Biomed Pharmacol J 2019;12(1). Available from: https://bit.ly/2XE3Emn |
Introduction
Several cytotoxic drugs are being used as cancer chemotherapeutics as well as for long term immunosuppressive therapy in organ transplant subjects.1 Cyclophosphamide is most commonly used chemotherapeutic drug against a variety of cancers and disorders like systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis and multiple sclerosis but has toxic effects on normal cells too.2-4 Apart from its therapeutic efficacy, its immunosuppressive and cytotoxic effects bring an impairment of host defence mechanism leading to significant morbidity and mortality which is a major limiting factor in cancer treatment. 5 The toxic effects of cyclophosphamide (CP) are mainly due to generation of its active metabolites namely phosphoramide mustard and acrolein, the most toxic agent.6 The molecular mechanism of CP inducing immunosuppression has been explained by Huang and Li in 20137 As IL-10 and IFN –γ play an important role in cyclophosphamide induced immunosuppression, the model of CP induced immunosupression is employed to evaluate the potential immunomodulatory effects of test substances.8-10 Hence, discovery of new immunopotentiating agents with detoxification properties would have potential beneficial effects in cancer treatment.
A large number of plants such as Tinospora cordifolia, Moringa indica, Ocimum sanctum, Azadirachta indica, Abulitum indicum, Curcuma longa, Moringa Olifera, Centilla aciatica have been shown to possess a wide array of immunomodulatory effects in rat and mice.11 Many studies have reported that combining certain plant products with chemotherapy may improve quality of life, tumour response and reduce toxicities of chemotherapy.eg Ganoderma lucidum,5 Kigelia africana,12 Onion lectin1 hemicellulose of bamboo shavings,8 Decalepis hamiltonii13,14 Roscorea procera rhizomes15 etc.
Gymnema sylvestre R Br. (Family Asclipedeceae) leaves, commonly known as Gudmar has been widely used in Indian Ayurveda traditional medicine to treat diabetes, obesity and asthma.16 The leaves of this plant has also been used as anti-inflammatory, astringent, anodyne, digestive and liver tonic.17 The effect of Gymnema leaf extract on fat and glucose metabolism is also reported.18 In some in – vitro experimental models the immunostimulatory effect of Gymnema has been observed11 and hence this activity in in-vivo models needs to be explored. With this background, the present study was aimed to investigate the immunomodulatory activity of hydro-alcoholic extract of Gymnema sylvestre leaves using experimental models of cyclophosphamide-induced immunosuppression in Wistar albino rats.
Materials and Methods
Plant Material
The hydroalcoholic extract of leaves of plant Gymnema sylvestre were procured from Indian Herbs Saharanpur (UP)
Animals
Thirty wistar albino rats of either sex of 2-3 months old (weighing between 120-150gms) were procured from a registered breeder. (no.526/02/bc/CPCSEA) The animals were housed in central animal house of MKCG Medical College Berhampur (Regd No. 472/CPCSEA/) and maintained at 22±1º C with 55±10% relative humidity and 12/12 hour light/ dark cycle. All rats were fed with standard pellet diet and water ad libitum. The animals were allowed to acclimatize to laboratory conditions one week prior to the day of experimentation. Prior to the experimentation, the experimental protocol was approved by the Institutional Animal Ethics Committee (IAEC) and care of animals was taken as per CPCSEA guidelines.
Drugs and Chemicals
All the drugs and chemicals were of analytical grade. Levamisole (Khandewal pharmaceutical Ltd. Mumbai), cyclophasphamide (Biochem Pharmaceutical, Mumbai), colloidal carbon (Indian Ink, camel India pvt. Limited), Alsevers solution and Phosphate buffer saline were procured from Hi-Media Laboratories Pvt. Limited.
Test Compound Preparation
The dilution of hydro-alcoholic extract of Gymnema sylvestre leaves was prepared in 1% gum acacia prior to oral administration. Freshly prepared solution was used for experiment.
Acute Toxicity Study
Acute toxicity study was done as per OECD guidelines 423 [limit test].19 The extract at doses 5, 50, 1000 and 2000 mg/kg were given orally to different group of overnight fasted rats. The animals had free access to water only. The animals were observed for 24 hours. There was no mortality or behavioural changes observed during the study period.
Phytochemical Screening of Plant Material
Preleminary phytochemical screening of hydro-alcoholic extract of this plant revealed presence of alkaloids, triterpenoids, flavonoids, steroids, tannins and phenolic compounds.
Experimental Design
The rats were randomly divided into five different groups for each experimental model. All the drugs and vehicles were given orally for 21 days. On 9th and 16thday of study, cylophosphamide was injected intraperitoneally (i.p) at a dose of 100mg/kg to all the rats except that of Gr-I (control)[20].
Gr.I- (Control) Received vehicle, 1% gum acacia.
Gr.II- (Disease control) received Cyclophosphamide -100mg/kg ip and1% gum acacia orally.
Gr.III- (standard) Cyclophosphamide + Levamisole- 50mg/kg.
Gr.IV -Cyclophosphamide+Gymnema sylvestre -25mg/kg.
Gr.V – Cyclophosphamide+Gymnema sylvestre -50mg/kg.
Experimental Procedure
Preparation of Sheep RBC Antigen
For this purpose, 5 ml of sheep blood was collected in sterile Alsevere’s solution in 1:1 preparation and centrifuged at 2000rpm for 10 minutes. Then it was washed with buffer saline (PBS) for 4-5 times and kept in refrigerator for further use. On the day of experiment, the RBC suspension was adjusted to a concentration of 0.5 X 109 cells after RBC count in Neubers chamber. This suspension was used for immunisation and antigen challenge.21,22
Body and Organ Weight
The initial body weight of each animal was weighed before starting the experiment and weighed at weekly interval after administration of drug or vehicle. At the end of experiment, the animals were sacrificed. The liver, spleen and kidney were removed and weighed immediately.
Haemagglutination Ab (HA) Titre
On 14th day of drug treatment, rats of all the groups were immunized with 0.5X 109 sheep RBC intraperitoneally. The day of immunization was referred as day 0. The drug treatment was continued for another 7 more days. On 21st day, 1 hour after the last test dose, blood samples were collected from retro orbital plexus and serum was separated.
The Ab titre was determined by challenging 25 µL of two fold diluted sera with 0.025X109 Sheep RBC suspensions in 96 well microtitre plates. PBS was used as diluents in all samples. The plates were incubated at 37oC for 1hr and then observed for haemagglutination. The highest dilution showing haemagglutination was taken as Ab titre.23
Delayed Type Hypersensitivity (DTH) Response
On 7th day of treatment the paw volume of right hind foot pad of all rats were measured using plethysmometer by mercury displacement method. The animals were then immunized by injecting 20µl of 0.5X109 SRBC’s intra-peritoneally. On 21st day of drug treatment, all rats were challenge with 0.025 X 109 SRBC S.C into right hind paw. After 24 and 48 hr of challenge, the right hind paw volumes were measured again. The difference between pre and post challenge paw volumes was expressed as DTH reaction.23,24
Neutrophil Adhesion Test
On day 14, from all rats the blood samples from retro orbital puncture were collected in EDTA containing vials and analyzed for TLC, Differential count(DLC). After initial count, blood samples were incubated with 80mg/ml of nylon fiber at 37°C for 15mins. The incubated blood samples were again analyzed for TLC and DLC
The product of TLC and % Neutrophil gives Neutrophil index of the sample.25
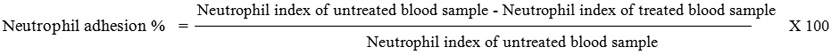
Carbon Clearance Test
The animals were divided into five groups and drug or vehicle treatment was given for 21 days exactly as per the above experimental design. On 21st day, 3 hours after the last dose all the animals of each group were injected intravenously (tail vein) with carbon ink suspension (1:50 dilution of Indian ink, Camel) in a dose of 0.5 ml/ 100gm body weight. Blood was withdrawn from retro-orbital venous plexus (25µl) at 0 and 15 minutes after injection of colloidal carbon ink and was lysed with 0.1% of sodium carbonate solution (3ml). The optical density was measured spectrophotometrically at 650 nm. [24, 26] The Phagocytic index (K) was calculated using the formula:
K = (ln OD1-ln OD2) / t1-t2
Where OD1 and OD2 are the optical densities at time t1 and t2 respectively.
Statistical Analysis
The data were analyzed by One-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey’s multiple comparison‘t’ test using Graph pad Prism version 7.0 Values of p < 0.05 were considered to be the minimum level of significance.
Results
Effect on Lymphoid Organ Weight
The relative weights of liver spleen and kidney with respect to their body weights in CP control rats were significantly reduced in comparison to normal control rats. (p<0.001) With treatment of levamisole, and GSE 25 as well as 50 mg/kg the relative organ weights were significantly increased in comparison to that of CP treated rats as shown in Table 1.
Table 1: Effect of different drugs and vehicle on relative organ weights of rats.
| Group | Drug and dose | Mean relative organ weight (mg/ 100gm B.W.) ± SEM | ||
| Spleen | Liver | Kidney | ||
| I (Control) | 1% Gum Acacia- 0.5ml/ Rat orally | 0.52±0.029 | 4.77±0.293 | 0.87±0.027 |
| II- CP control | 100mg/kg (i.p) +GA 0.5 ml orally | 0.21±0.029a | 2.46±0.233a | 0.56±0.024a |
| III | CP+LEV -50 mg/kg | 0.41±0.0149c | 4.16±0.197c | 0.76±0.202c |
| IV | CP+GSE-25mg/kg | 0.30±0.009b | 3.40±0.178b | 0.65±0.021 |
| V | CP+GSE-50mg/kg | 0.39±0.013c | 3.81±0.152b | 0.72±0.021c |
n=6 in each group. One way ANOVA test reveals – a: p<0.05 vs normal control, b- p<0.05, c- p<0.001 vs CP control group.
Effect on Humoral Immunity
Administration of Cyclophosphamide decreased HA titre to a highly significant extent as compared to that of control rats. (p <0.001) The mean Ab titre of control rats was 138.7±25.69 whereas the CP treated rats had 24.0±3.58. Levamisole increased HA titre (106.7±13.4) to a highly significant extent in CP induced immunosuppressed rat when compared to that of CP treated control rats. (p<0.001) But this effect is not comparable to that of normal rats. GSE with 50 mg/kg , significantly increased the HA titre to 85.33±13.49 in comparison to CP control group of rats (p<0.01) revealing stimulation of humoral immune response to sheep RBC (Table 2).
Table 2: Effect of different drugs and vehicle on haemagglutination titer, percentage neutrophil adhesion and phagocytic index in rats.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
| Group | HA titer | % NA | Phagocytic Index |
| I(control) | 138.7±25.69 | 28.47±2.06 | 0.068±0.0633 |
| II(CP) | 24.0±3.58a | 13.25±1.18a | 0.026±0.0031a |






