Manuscript accepted on :28 April 2018
Published online on: 07-05-2018
Plagiarism Check: Yes
Girija Kumari1, 2 , Vikram Singh1,3
, Vikram Singh1,3 , Saurabh Dahiya1
, Saurabh Dahiya1 , Ashok Kumar Jhingan2
, Ashok Kumar Jhingan2 and Bimal Chhajer3
and Bimal Chhajer3
1Department of Pharmacy, Lingaya’s University, Faridabad (Haryana) 121002, India.
2Department of Medicine, Delhi Diabetes Research Center, New Delhi (Delhi) 110027, India.
3Department of Preventive Cardiology, SAAOL Heart Center, New Delhi (Delhi) 110030, India.
Corresponding Author E-mail: saurabhdahiya@gmail.com
DOI : https://dx.doi.org/10.13005/bpj/1432
Abstract
Diabetes is a costly, lifestyle disorder which increases the burden of disease and deteriorates the Health-Related Quality of Life (HRQOL) of diabetes patients and this study was conducted to assess the effect of lifestyle intervention on medical treatment cost and HRQOL in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients. This quasi-experimental prospective study was conducted in Delhi Diabetes Research Center, New Delhi and included 224 T2DM patients. Patients were divided into LMC and usual care group on the basis of receiving or not receiving lifestyle modification counseling. The follow-up of both groups was done at 6th and 12th months. Collected data were analyzed through IBM, SPSS software v 21 for mean, median (min-max), SD, t-test and Wilcoxon scores (rank sums) test. The results of this study showed a statistically significant reduction in diabetes medication costs, hospitalization and surgery costs in the LMC group as compared to the usual care group. The significant improvement was also observed in HRQOL domains which includes - physical functioning (62.40±6.738 to 83.67 ± 5.4920), physical health (35.30±22.069 to 64.50±13.62), emotional problem (37.90±28.93 to71.46±16.75), energy (54.31±11.858 to 80.75 ± 15.52), emotional well-being (63.06± 9.828 to 85.79±6.36), social functioning (38.848±20.805 to 65.54±8.39) and general health (54.51±11.679 to 82.398± 11.7) at 12th month follow up in LMC group. The ADS score also showed significant improvement in overall HRQOL of LMC group. This study concludes that lifestyle intervention may improve HRQOL and reduce medical treatment cost of T2DM patients.
Keywords
Lifestyle Intervention; Health-Related Quality of Life; Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus; Appraisal Scale of Diabetes; Treatment Cost; SF-36
Download this article as:| Copy the following to cite this article: Kumari G, Singh V, Dahiya S, Jhingan A. K, Chhajer B. Effect of Lifestyle Intervention on Medical Treatment Cost and Health-Related Quality of Life in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients. Biomed Pharmacol J 2018;11(2). |
| Copy the following to cite this URL: Kumari G, Singh V, Dahiya S, Jhingan A. K, Chhajer B. Effect of Lifestyle Intervention on Medical Treatment Cost and Health-Related Quality of Life in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients. Biomed Pharmacol J 2018;11(2). Available from: http://biomedpharmajournal.org/?p=20316 |
Introduction
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a non-infectious, silent, metabolic disorder, develops due to increasing age, obesity, unhealthy diet, physical inactivity, stress and consumption of tobacco.1,4 Presently, more than 415 million people are diabetic globally as per International Diabetes Federation (IDF) and this number is expected to increase to 642 million by 2040. Due to increasing prevalence and, the high population, India has become the ‘Diabetic Capital’ of the world and having the second highest number (69.1 million) of diabetes patients after China.2,4 Diabetes is a costly lifestyle disorder associated with various long-term, macro (cardiovascular diseases) and microvascular (retinopathy, nephropathy, and neuropathy) complications. These complications, lower the quality of life of T2DM patients and increase the rate of morbidity and mortality.3,4The cost of diabetes treatment is increased due to long-term complications and co-morbidities, which exert enormous economic burden, both for the individual and the nation.5 Diabetes is the most common cause of death and disability around the world, caused due to secondary lifestyle and rapid globalization. Around 75% T2DM patients live in low and middle-income countries.4 India is a low and middle income developing country, where diabetes treatment cost is increasing day by day and patients faced the huge cost burden due to out of their pocket expenditure.1,5 The global economic burden of diabetes is huge with an estimated approximately 673 billion US dollars annually in 2015, which constituted 12% of total expenditure for that year.1,4The public health expenditure on diabetes is expected to rise to the US $ 595 billion in 2030 and the disease can be considered a risk for the world.6,7
WHO defined that health is not only the absence of disease and frailty in the body but also physical, mental and social well-being, must be present in a healthy person. The HRQOL is an important health outcome and used to assess the physical and mental health status of a person.8The relationship between HRQOL and the number of chronic complications found a trend towards poorer HRQOL if co-morbidities increased.9,10 Poor QOL of patients occurred due to non-adherence to medication and self-management, which leads to uncontrolled diabetes and increased the risk of fetal complications.11 A study demonstrated that diabetes can affect QOL in many ways: psychologically, physically, financially and socially.7
Medical treatment costs and HRQOL have shown a direct relationship. Diabetes treatment cost will be higher if the duration and number of complications due to diabetes increased, HRQOL of patients deteriorates.12,13A survey done by Piette et al found that 30% of patients had difficulties in paying diabetes medication costs due to out-of-pocket money14 and other study revealed that out-of-pocket costs were due to diabetes-related complications and co-morbidities and experienced worse diabetes outcomes with poor QOL.15 Lifestyle modification counseling (LMC) is the key component to achieve better glycemic control, improve HRQOL and reduce diabetes treatment cost due to the reduction of complications.16Educated diabetic patients can develop the skills that allow them to cope with diabetes and its related complications.17 Hence, Lifestyle modification counseling generally used as an intervention is a novel, cost-effective, non-invasive method to manage T2DM and decrease the rate of complications. LMC includes- education about self-management, healthy diet, physical activity, tobacco and smoking cessation, stress management counseling with routine medical checkups and medication adherence counseling. The purpose of this study was to assess the effect of lifestyle intervention on medical treatment cost and health-related quality of life in T2DM patients.
Materials and Methods
This hospital-based quasi-experimental, prospective study was conducted in DDRC New Delhi. In this study, total 224 T2DM patients were enrolled based on consecutive sampling technique. The study participants were allocated to LMC group and the usual care group on the basis of patients receiving or not receiving lifestyle modification counseling. LMC group received lifestyle modification counseling with standard care (pharmacological treatment) while usual care group received only pharmacological treatment. The study was conducted in two phases. In the first phase planning, preparation for counseling components and recruitment of participants was done and in the second phase the implementation of counseling, data collection, follow-ups, and data analyses.
Eligibility Criteria
The patients who included in this study were clinically and diagnostically confirmed T2DM, either sex, aged between 35 to 70 years, having blood sugar fasting more than 120 mg/dl, blood sugar PP more than 180 mg/dl, and HbA1c above 7%. Patients having at least one co-morbidity (obesity, hypertension, coronary heart disease) with T2DM and having diabetes more than 1 year, willing to participate and able to give valid written consent. The patients who excluded were newly diagnosed, having Type 1 and gestational diabetes, kidney failure, hospitalized, received more than one-time lifestyle intervention counseling within 1 year and having the mental disorder, visual, hearing problems and unwilling to give written consent.
Recruitment of study Participants
Total 224 T2DM patients were enrolled as they fulfilled study eligibility criteria. The total duration of the study was 2 years (2015 to 2017) with one-year follow-up. The sample size (n=224) was calculated with an allowable error of 20% and 5% level of significance using below given standard formula.
formula
Where p= (p_t±p_s)/2, pt is the proportion of LMC group and ps is the proportion of usual care group.
Lifestyle Intervention
Lifestyle modification counseling was used as an intervention tool for participants to prevent and control T2DM. The counseling program was initiated in two phases. The first six months of the study were active period and next six months of the maintenance period, i.e. Interventional counseling was provided to the participants for previous 6 months. The LMC sessions were provided by an experienced and qualified dietitian, physical trainer and diabetes educator, under the supervision of senior diabetologist. The following five-lifestyle components were explained in local language, with the help of pictures, videos and discuss with participants and the group of the participant. Lifestyle modification counseling (intervention) was repeated at every month for 6 months and follow up with the participants were done at 6th and 12th month.
Key Components of the Intervention
Balanced Diet
A qualified and experienced dietician encouraged participants to cut down high-calorie foods and advised to increase the number of fibrous foods (whole grain, green vegetables, and fruits). Participants were advised to adhere to the diet chart prescribed by the dietitian.
Physical Activity
Participants were motivated by a physical trainer to increase their physical activities, i.e. brisk walk for at least 30 minutes per day and to do daily yogic exercises for at least 30 minutes (Yoga- Mudrasana, Balasana, Vajrasana, Paschimottanasana, Ardha Matsyendrasana, Supta Vajrasana, Dhanurasana, Shavasana).
Tobacco and Alcohol Cessation
Participants were motivated to quit tobacco (smoking and chewing tobacco) and alcohol at every counseling session. They were educated about the harmful effects of tobacco and alcohol.
Stress Management
Participants were encouraged to do daily meditation and breathing exercise at least for 15 minutes to control stress and advice were given to take proper sleep.
Adherence to Routine Medical Checkups and Medications
Diabetologist advised the participants to adhere on routine medical checkups (the clinical assessment with blood sugar fasting, PP, HbA1c, lipid profile) and regular medications without skipping.
Usual Care Group
Participants in the usual care group received only standard treatment. In addition, they were also provided the pamphlets and booklets for self-management of diabetes. A diary was provided to record their weight, diets, physical activities and other blood test results as it was also provided to LMC group.
Measurements
Demographic and socioeconomic details (Age, sex, locality, medical history, education, occupation, monthly income and socioeconomic status) of both the groups had been done at baseline.
Treatment cost Assessment
The cost of medical treatment for diabetes and its related complications was analyzed through diabetes and its related complications questionnaire.
Health-Related Quality of Life (HRQOL)
The HRQOL of our study participants of both the group was measured through short-form health survey (SF-36) questionnaire and a disease-specific questionnaire, appraisal of diabetes scale (ADS). Quality of life of T2DM patients was assessed by asking questions to participants, whether they experienced problems related to life, such as mobility, personal care, housework, family, study, leisure activities, pain, discomfort and anxiety/depression. Responses were recorded as the answers. SF-36 contains 36 questions of eight health domains; physical functioning, physical limitation, emotional limitation, vitality, emotional well-being, social functioning, body pain and general health.18 The eight domains were scored from 0 to 100 indicating worst to best possible health.
ADS is a diabetes-specific scale to assess QoL of diabetes patients have 7 items covering domains; stress due to diabetes, uncertainty, control over diabetes (2 questions), predictable future deterioration, coping skill and diabetes effect on life goals. The total score can range from 0 to 35. Thus, the lower score on ADS scale suggests better QOL.19
Statistical Analysis
Statistical package for the social sciences (SPSS) software version 21 was used for all statistical analyses. Participants’ demographic and socioeconomic measurements were compared between groups using independent t-test. Descriptive analysis (Mean, Median (Min-Max), SD), Chi-square, sample paired and independent t-test was used to analyze data with 95 % confidence interval and a significant p-value less than 0.05. Medical treatment cost was assessed through Wilcoxon scores (rank sum) test to calculate p-value as data was not normally distributed.
Ethical Approval and Consent
Ethical clearance for this study was obtained from DDRC, New Delhi, and SAAOL Heart Center (Ref. No. IEC/SHRF/PhD/P-01/29.04.2016), New Delhi. Written informed consent was obtained from all study participants before initiation of the study.
Results
Recruitment and Response Rates of the Participants
Total 312 type 2 diabetes mellitus patients were screened from DDRC, New Delhi. 224 participants were enrolled as they fulfill study eligibility criteria and agree to complete follow-up. Remaining 88 patients were excluded because 12 patients were having diabetes for less than one year, 27 patients refused to give consent, 33 refused to participate and follow-ups and 16 patients were having time commitment difficulty. Patients were allocated to LMC and the usual care group. Each group had 112 patients. 10 patients did not complete 12-month study follow-ups from LMC group and 12 patients from the usual care group were excluded because patients did not complete follow-ups. Finally, 202 (n=100 in the usual care group and n=102 in LMC group) patients have completed the whole study with 6 and 12- month follow-up. A summary and study overview is given in Figure 1.
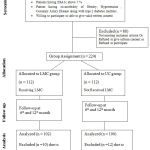 |
Figure 1: Recruitment and response rates of the study participants |
Baseline Characteristics of Participants
The mean (SD) age of the participants was 52.7±9.1years with age range from 35 to 70 years. The number of male participants was higher 118 (58.4%) than females 84 (41.6%). A larger number of participants were from urban (111) area as compared to rural and semi-urban 42 and 49 respectively. Patients were from the various types of occupations, most of the patients were unemployed (retired and females) (70) followed by clerical/shop owner (41). A statistically significant difference was found in income-group and most of the patients were from the income group of 19291-38599 INR followed by income group of >38,600 INR. The majority of patients were suffering from obesity (127) and hypertension (150) followed by heart disease (68). In this study, 77 patients were having a family history of diabetes and half (50%) of patients were non-vegetarian. Total 51 patients were consuming alcohol followed by tobacco chewing in 24 patients, 31 were the smoker, and no statistical difference was observed in the LMC and the usual care group. The baseline characteristics and socioeconomic profile of study subjects are presented in Table 1 & 2.
Table 1: Baseline demographic characteristics of study participants
| Characteristics | Total (n=202) | Usual Care Group (n=100) | LMC group
(n=102) |
p-value | |||
| Age (in years) | 52.7±9.1 | 54.0±8.6 | 51.4±9.3 | 0.336 | |||
| Gender | |||||||
| Male (n) | 118 | 61 (51.7%) | 57 (48.3%) |
0.276 |
|||
| Female (n) | 84 | 39 (46.4%) | 45 (53.8%) | ||||
| Locality | |||||||
| Rural | 42 | 10 (23.8%) | 32 (76.2%) |
0.001 |
|||
| Urban | 111 | 55 (49.5%) | 56 (50.5%) | ||||
| Semi-Urban | 49 | 35 (71.4%) | 14 (28.6%) | ||||
| Present Status of Health | |||||||
| Obesity | 127 | 59 (59%) | 68 (66.67%) | 0.757 | |||
| Hypertension | 150 | 75 (75%) | 75 (73.53%) | 0.973 | |||
| Heart Disease | 68 | 30 (30%) | 38(37.25%) | 0.489 | |||
| Family History of Diabetes | |||||||
| Yes | 77 | 38 (49.4%) | 39 (50.6%) |
0.973 |
|||
| No | 125 | 62 (49.6%) | 63 (50.4%) | ||||
| Risk Factors | |||||||
| Smoking | 31 | 21(21%) | 10 (9.8%) | 0.257 | |||
| Tobacco chewing | 24 | 13 (13%) | 11 (10.78%) | 0.814 | |||
| Alcohol | 51 | 30 (30%) | 21 (20.58%) | 0.649 | |||
| None | 114 | 47 (47%) | 67 (65.68%) | 0.290 | |||
| Food Habits | |||||||
| Vegetarian | 90 | 45 (50.0%) | 45 (50.0%) |
0.609 |
|||
| Non-vegetarian | 112 | 56 (50.0%) | 56 (50.0%) | ||||
| Duration of Diabetes (years) | Mean±SD | Median
(Min- Max) |
Mean±SD | Median
(Min- Max) |
Mean±SD | Median
(Min- Max) |
p-value |
| 7.9±6.2 | 7 (1-27) | 7.9±6.4 | 7 (1-27) | 7.93 (1-27) | 7(1-27) | 0.797 | |
Table 2: Baseline socioeconomic profile of study participants
|
Education Total |
LMC Group
(n=102) |
UC Group
(n=100) |
p-value | ||||
| Number | Percentage % | Number | Percentage % | ||||
| Illiterate | 2 | 2 | 100.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.471 | |
| Upto class 5 | 10 | 6 | 60.0 | 4 | 40.0 | ||
| Upto class 8 | 11 | 7 | 63.6 | 4 | 36.4 | ||
| Upto class 10 | 45 | 26 | 57.8 | 19 | 42.2 | ||
| 12th or diploma | 69 | 35 | 50.7 | 34 | 49.3 | ||
| Graduate/Post-graduate | 63 | 33 | 52.9 | 30 | 47.1 | ||
| PhD/Doctorate | 2 | 1 | 50.0 | 1 | 50.0 | ||
| Occupation | |||||||
| Unemployed | 70 | 34 | 48.6 | 36 | 51.4 | 0.003 | |
| Unskilled worker | 18 | 17 | 94.4 | 1 | 5.6 | ||
| Semi-Skilled worker | 13 | 7 | 53.8 | 6 | 46.2 | ||
| Skilled worker | 21 | 12 | 57.1 | 9 | 42.9 | ||
| Clerical, Shop owner | 41 | 18 | 43.9 | 23 | 56.1 | ||
| Semi professional | 36 | 12 | 33.3 | 24 | 66.7 | ||
| Professional | 3 | 2 | 66.7 | 1 | 33.3 | ||
| Monthly income | |||||||
| >38,600 | 61 | 29 | 47.5 | 32 | 52.5 | 0.001 | |
| 19291-38599 | 75 | 35 | 46.7 | 40 | 53.3 | ||
| 14463-19290 | 25 | 22 | 88.0 | 3 | 12.0 | ||
| 9634-14462 | 3 | 3 | 100.0 | 0 | 0.0 | ||
| 5773-9633 | 4 | 3 | 75.0 | 1 | 25.0 | ||
| 1933-5772 | 2 | 2 | 100.0 | 2 | 0.0 | ||
| <1932 | 32 | 8 | 25.0 | 24 | 75.0 | ||
| Socio-economic status | |||||||
| Upper Class | 77 | 32 | 41.6 | 45 | 58.4 | 0.001 | |
| Upper Middle | 96 | 43 | 44.8 | 53 | 55.2 | ||
| Lower Middle | 25 | 24 | 96.0 | 1 | 4.0 | ||
| Upper Lower | 3 | 3 | 100.0 | 0 | 0.0 | ||
| Lower | 1 | 0 | 0.0 | 1 | 100.0 | ||
Cost Analysis of Various Expenditures of Diabetes and Diabetic Complications
At 12 month follow up, the result of the present study reveals that the LMC group (9627.5 ± 1938.4) spends less money on diabetes medicine as compared to the usual care group (10534.0 ± 2169.4) with significant p-value 0.0038.The surgery cost of usual care group (9212.0 ± 17464) was higher due to diabetes complications as compared to the surgery cost of LMC group patients (3186.3 ± 10595) with significant difference p 0.0046. The average hospitalization cost of usual care group (39580 INR) was approximately four times higher as compared to LMC group (10569 INR). The average mean (SD) of some variables including; other expenses for diabetes (340.0 ± 573.7 vs 173.5 ± 359.0), diabetes neuropathy expenses (307.0 ± 1031.0 vs 184.3 ± 569.6), hypertension medicines cost (257.8 ± 429.6 vs 173.8 ± 267.2), diabetes retinopathy expenses (39.0 ± 390.0 vs 14.7 ± 106.6), foot complication related treatment cost (305.5 ± 976.1 vs 137.8 ± 483. 2) showed mean change, but that did not reach to the statistically significant level. Whereas LMC group spend more money on doctor’s consultation fees for diabetic complications because of the LMC group participants have more diabetic complications. Travel cost, laboratory cost, diabetes complications diagnostics cost and heart disease medicines cost were slightly higher in the LMC group because of the higher number of heart disease patients present in the LMC group as compared to the usual care group. Details of the results are given in Table 3.
Table 3: Medical Treatment cost assessment at 12 months of usual care & LMC group of T2DM patients
| Expenditure (INR) | UC Group (n=100) | LMC Group (n=102) | p-value* | ||
| Mean ± SD | Median
(Min-Max) |
Mean ± SD | Median
(Min-Max) |
||
| Travel Cost | 1146.7 ± 520.5 | 875 (420-2170) | 1200.39 ± 537.59 | 1455 (600-2350) | 0.822 |
| Laboratory cost | 1099.2 ± 260.93 | 1120 (640-1920) | 1112.16 ± 291.28 | 1120 (620-1920) | 0.739 |
| Medicine cost | 10534.0 ± 2169.35 | 10050 (6850-17200) | 9627.45 ± 1938.42 | 9400 (5890-15400) | 0.004 |
| Hospitalization cost | 80727.27 ± 85023.63 | 38000 (21000-42000) | 43120 ± 55805.7 | 25000 (18500-48600) | 0.011 |
| Surgery Cost | 41900 ± 14237.57 | 42500 (28500-45800) | 36111.11 ± 8922.5 | 38000 (26200-44700) | 0.005 |
| Other expenses for diabetes | 880 ± 482.58 | 750 (560-1020) | 737.5 ± 363.3 | 500 (400-1210) | 0.104 |
| Diabetes Complication – Doctor fees | 3432.25± 1779.21 | 2400 (2200-6400) | 4054.9 ± 1755.81 | 4000 (1820-7000) | 0.087 |
| Diabetes Neuropathy expenses | 1650 ± 1369.91 | 1200 (800-2200) | 1880 ± 315.52 | 1900 (820-2400) | 0.882 |
| Hypertension medicines cost | 950 ± 117.59 | 950 (840-1060) | 537.27 ± 155.04 | 540 (310-1170) | 0.632 |
| Heart disease medicines cost | 7593.75 ± 216.19 | 7550 (6900-8100) | 6918.18 ± 144.59 | 7000 (6750-8000) | 0.653 |
| Diabetes Retinopathy expenses | 900± 141.42 | 900 (720-1080) | 750 ±212.13 | 750 (500-1120) | 0.504 |
| Foot complication related treatment cost | 3300 ± 141.42 | 3300 (3100-3820) | 1756.25 ±345.82 | 1750 (1210-3600) | 0.635 |
| Diabetes Complications Diagnostics cost | 1923.81 ± 871.15 | 1300 (1080-2040) | 1894.54 ± 807.01 | 2100 (1250-2800) | 0.551 |
*Wilcoxon scores (rank sums) test was used to calculate p-value as cost data was not normally distributed.
Effects of lifestyle intervention on health-related quality of life
On the assessment of the SF-36 questionnaire after 6 months, the LMC group participants showed significant improvement in the physical functioning, role limitation due to emotional problems, energy/fatigue, emotional well-being, and social functioning after 6 months with all significant p-values 0.0001 as compared to the usual care group. There was no statistically significant improvement observed in body pain, role limitation due to physical health and general health at 6-month follow up. At 12 month LMC group achieved significant improvement in physical functioning (62.402±6.7388 to 83.676 ± 5.4920), Role limitation due to physical health (35.30±22.069 to 64.50±13.62 ), role limitation due to emotional problem (37.90±28.93 to 71.46±16.75), energy/fatigue (54.31±11.858 to 80.75±15.527), emotional well-being (63.06±9.828 to 85.79±6.36), social functioning (38.848±20.8058 to 65.54±8.39) and general health (54.51±11.679 to 82.398± 11.7) from baseline to 12 months with significant outcomes (p-value less than 0.05) as compared to the usual care group. There was no significant improvement has been observed in bodily pain (68.701±14.5295 to75.123±13.35) at 12 months follow up. Details are given in Table 4.
Table 4: Changes in SF-36 QoL of participant’s measurements from baseline to 6th and 12th month follow-up with differences in within and between groups over time
| Variables | UC Group
(n=100) |
LMC group
(n=102) |
Difference between the group
(p-value) |
||||||
| Mean±SD | Median (Min-Max) | Mean±SD | Median
(Min-Max) |
||||||
| Physical Functioning
Baseline 6 Month 12 Month |
61.15±9.66
69.52±9.97 58.20±9.035 |
60 (45-75)
70 (30-90) 60 (35-80) |
62.40±6.73
65.53±8.38 83.67± 5.49 |
62 (40-80)
66 (32-85) 83 (30-90) |
0.288
0.002 0.0001 |
||||
| Difference within group (p-value) | B-6M
B-12M |
0.0001 | 0.003 | ||||||
| 0.027 | 0.0001 | ||||||||
| Role Limitation due to Physical Health
Baseline 6 Month 12 Month |
35.25 ±24.12
44.90±25.88 35.77±23.62 |
32 (30-68)
42 (35-70) 35 (30-80) |
35.30±22.06
44.36±22.50 64.50±13.62 |
35 (25-75)
44 (35-70) 64 (40-80) |
0.989
0.894 0.0001 |
||||
| Difference
within group (p-value) |
B-6M
B-12M |
0.008 | 0.005 | ||||||
| 0.877 | 0.0001 | ||||||||
| Role Limitation due to Emotional Problem
Baseline 6 Month 12 Month |
37.33±30.80
38.00 ±29.21 42.66±30.36 |
36 (30-70)
38 (30-80) 40 (35-85) |
37.90±28.93
54.24±26.91 71.46±16.75 |
36 (30-70)
52 (30-90) 71 (40-95) |
0.891
0.0001 0.0001 |
||||
| Difference
within group (p-value) |
B-6M
B-12M |
0.882 | 0.0001 | ||||||
| 0.222 | 0.0001 | ||||||||
| Energy / Fatigue
Baseline 6 Month 12 Month |
53.00±11.76
57.00±11.43 60.15±12.60
|
55 (25-80)
57 (30-85) 59 (30-80) |
54.31±11.85
60.34±12.55 80.75± 15.52 |
54 (20-80)
60 (30-85) 80 (30-90) |
0.430
0.049 0.0001 |
||||
| Difference
within group (p-value) |
B-6M
B-12M |
0.007 | 0.001 | ||||||
| 0.0001 | 0.0001 | ||||||||
| Emotional Well being
Baseline 6 Month 12 Month |
64.48±13.62
68.24± 9.82 69.52±9.98 |
66 (45-100)
67 (30-90) 69 (30-85) |
63.06± 9.82
82.40± 11.78 85.79±6.36 |
64 (40-100)
80 (30-100) 84 (20-100) |
0.413
0.0001 0.0001 |
||||
| Difference
within group (p-value) |
B-6M
B-12M |
0.035 | 0.0001 | ||||||
| 0.0001 | 0.0001 | ||||||||
| Social Functioning
Baseline 6 Month 12 Month |
43.875±19.98
49.250±18.87 51.125±16.77 |
43 (12-87)
49 (15-82) 51 (12-90) |
38.84±20.80
42.52± 11.96 65.54±8.39 |
40 (12-90)
42 (20-92) 67 (20-90) |
0.082
0.003 0.0001 |
||||
| Difference
within group (p-value) |
B-6M
B-12M |
0.036 | 0.095 | ||||||
| 0.002 | 0.0001 | ||||||||
| Bodily Pain
Baseline 6 Month 12 Month |
68.250± 14.50
68.800± 17.18 71.450±16.74 |
68 (45-95)
69 (45-90) 71 (45-95) |
68.70±14.52
71.17± 16.69 75.12±13.35 |
68 (40-95)
71(30-100) 76 (40-100) |
0.826
0.320 0.087 |
||||
| Difference
within group (p-value) |
B-6M
B-12M |
0.801 | 0.262 | ||||||
| 0.172 | 0.001 | ||||||||
| General Health
Baseline 6 Month 12 Month |
55.30±13.87
57.10±11.39 59.15±9.21 |
55 (30-85)
57 (25-85) 60 (30-80) |
54.51±11.67
59.56±10.88 82.39± 11.7 |
54 (30-80)
59 (25-85) 82(30-90) |
0.662
0.118 0.0001 |
||||
| Difference
within group (p-value) |
B-6M
B-12M |
0.265 | 0.001 | ||||||
| 0.021 | 0.0001 | ||||||||
As per as ADS score, patients of the LMC group showed statistically significant improvement at 6 months in all variables except in the first parameter (distress caused by diabetes). At 12 month follow up after lifestyle modification counseling most of the patients of LMC group showed significant improvement in all domains including distress caused by diabetes, uncertainty due to diabetes, control over diabetes, anticipated future deterioration, copying and effect of diabetes on life goals with statistically significant p values 0.05. Details of ADS are given in Table 5.
Table 5: ADS assessment at Baseline, 6th and 12th Months with significant differences within and between groups over study time in usual care and LMC group of T2DM patients
|
Q1 How upsetting is having diabetes for you? Baseline 6 Month 12 Month |
Usual Care Group
(n=100) Mean±SD Median (Min-Max) |
LMC Group
(n=102) Mean±SD Median (Min-Max) |
p-value between group
0.499 0.075 0.0001 |
|||
| 3.84±0.87
2.89±1.01 3.78±0.90 |
3 (1-5)
2 (1-5) 3 (1-5) |
3.90±0.29
3.07±0.27 2.80±0.67 |
3 (1-5)
3 (1-5) 2 (1-5) |
|||
| Difference
within group (p-value) |
B-6M
B-12M |
0.0001 | 0.0001 | |||
| 0.652 | 0.0001 | |||||
| Q2 How much control over your diabetes do you have?Baseline
6 Month 12 Month |
2.52±0.67
2.28±0.53 1.89±0.31 |
2(1-4)
2 (1-4) 1 (1-3) |
2.37±0.50
1.87±0.33 1.57±0.49 |
2 (1-4)
1 (1-3) 1 (1-3) |
0.80
0.0001 0.0001 |
|
| Difference
within group (p-value) |
B-3M
B-6M B-12M |
0.002 | 0.0001 | |||
| 0.0001 | 0.0001 | |||||
| Q3 How much uncertainty do you currently experience in your life as a result of being diabetic?
Baseline 6 Month 12 Month |
4.86±0.44
3.22±0.56 4.11±0.31 |
4 (1-5)
3 (1-5) 4(1-5) |
4.83±0.4
4.0±0.34 3.18±0.54 |
4 (1-5)
4 (1-5) 3 (1-5) |
0.657
0.0001 0.0001 |
|
| Difference
within group (p-value) |
B-6M
B-12M |
0.0001 | 0.0001 | |||
| 0.0001 | 0.0001 | |||||
| Q4 How likely is your diabetes to worsen over the next several years?
Baseline 6 Month 12 Month |
3.91±0.32
3.14±0.41 3.66±0.47 |
3 (1-5)
3 (1-5) 3 (1-5) |
3.74±0.79
2.91±0.28 1.90±0.49 |
3 (1-5)
2 (1-4) 1 (1-3) |
0.55
0.0001 0.0001 |
|
| Difference
within group (p-value) |
B-6M
B-12M |
0.0001 | 0.0001 | |||
| 0.0001 | 0.0001 | |||||
| Q5 Do you believe that achieving good diabetic control is due to your efforts as compared to factors which are beyond your control?
Baseline 6 Month 12 Month |
4.58±0.53
3.89±0.39 4.60±0.60 |
4 (1-5)
3 (1-5) 4 (1-5) |
4.62±0.50
2.12±0.33 2.09±0.29 |
4 (1-5)
2 (1-4) 2 (1-4) |
0.518
0.0001 0.0001 |
|
| Difference
within group (p-value) |
B-6M
B-12M |
0.0001 | 0.0001 | |||
| 0.783 | 0.0001 | |||||
| Q6 How effective are you in coping with your diabetes?
Baseline 6 Month 12 Month |
2.84±0.39
2.34±0.60 2.11±0.44 |
2 (1-5)
2 (1-5) 2 (1-5) |
2.91±0.28
2.09±0.29 2.90±0.29 |
2 (1-5)
2 (1-5) 2 (1-5) |
0.140
0.0001 0.0001 |
|
| Difference
within group (p-value) |
B-6M
B-12M |
0.0001 | 0.0001 | |||
| 0.0001 | 0.798 | |||||
| Q7. To what degree does your diabetes get in the way of your developing life goals?
Baseline 6 Month 12 Month |
3.24±0.62
3.03±0.33 2.37±0.67 |
3 (1-5)
3 (1-5) 2 (1-5) |
3.38±0.56
2.88±0.32 2.16±0.48 |
3 (1-5)
2 (1-5) 2 (1-5)
|
0.900
0.002 0.015 |
|
| Difference
within group (p-value) |
B-6M
B-12M |
0.006 | 0.0001 | |||
| 0.0001 | 0.0001 | |||||
Discussion
Effect of Lifestyle Intervention on Diabetes Medical Treatment Cost
Present study observed that patients in the usual care group who did not receive lifestyle modification counseling, spent more money on diabetes medicines as compared to LMC group and a significant difference has been observed with significant p-value 0.0038, similar finding of hospitalization cost with significant difference p-value 0.0111 and surgery cost due to diabetes complications was higher in the usual care group with significant difference p-value 0.0046 as compared to LMC group. The average hospitalization cost of usual care group (39580 INR) was approximately four times higher as compared to LMC group (10569 INR). As per our study diabetes treatment cost assessment, it can be concluded that lifestyle modification counseling used as the intervention was cost-effective therapy. Other similar lifestyle intervention studies done by Sevick et al, Upadhyay et al and Odnoletkova et al showed same evidence that lifestyle interventions were cost-effective among diabetes patients.20,22Studies done by Anne M et al and Wolf RD et al provided the evidence that lifestyle intervention reduces the risk of diabetes complications, improves quality of life and did so without increasing health care costs, similar to present study.23,24 A study by Png et al revealed that lifestyle intervention is cost-effective and can delay the risk of complications,25 and Katon et al demonstrated that adherence to self-management decrease disease burden, health care cost and frequent hospitalizations.26
Effect of lifestyle intervention on Health-Related Quality of Life (HR-QoL)
The results of our study did not show any significant difference at baseline in SF-36 domain scores. At the 6th month after lifestyle modification counseling, the participants of LMC group showed statistically significant improvement in the physical functioning, bodily pain, general health, and vitality from baseline to 6 months with all significant p-value less than 0.001 as compared to the usual care group. After 12 months of study follow up, the LMC group achieved significant improvement in all the domains, including physical functioning, role physical, bodily pain, general health, vitality, social functioning and mental health with significant p-values less than 0.001 as compared to the usual care group. As per ADS score, present study results did not show a statistically significant difference between LMC group and usual care group at baseline. After 6 months follow up the LMC group patients showed statistically significant improvement in all parameters except in one variable (distress caused by diabetes). At 12 months most of the patients of LMC group showed significant improvement in all domains with the significance p-value less than 0.05. Studies done by Norliza et al, Rajeshwari et al, and Kaskurthy et al studies have shown statistically significant improvement in glycemic control and overall QoL in T2DM patients after lifestyle modifications counseling provided by the pharmacist-patient counseling.27,29Similar studies by Testa et al, Shareef et al, and Sriram et al have shown significant improvement in the quality of life and significantly improved economic benefits after intervention.30,32Studies done by Reza et al and Adepu et al observed significant improvement in all domains of HRQOL in diabetes patients after educational counseling in test group participants.33,34 Studies conducted by Carvalho et al, Marzieh et al, and Alireza et al verified the influence of educational counseling and shown significant improvement in the overall QoL and HbA1c scores after counseling.35,37Similar studies by Ramune et al and Adibe et al showed significant improvements in HRQOL, and glycemic control, in T2DM patients.38,39In summary, our study concludes that LMC may improve overall HRQoL of T2DM patients and supported by above-discussed studies.
Study limitations
Due to limited resources and facilities, this study was not randomized designs, but a quasi- experimental study was designed in a standardized manner. There is need of multi-centric randomized trials to solve diabetes management queries.
Conclusion
Results of present study conclude that LMC is effective towards diabetes management and control and can reduce the medical treatment cost, improve HRQOL and coping skills of T2DM patients. Further multi-centric randomized control trials with the large population are required, to assess the effectiveness of lifestyle intervention on medical treatment cost and HRQOL in T2DM patients.
Conflict of Interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest related to the material presented in the present original manuscript.
References
- Norma S , Zaleha M.I and Azmi M T. The effect of life style intervention among pre- diabetes patients in Melaka, Malaysia. IOSR-JNHS. 2013;2:14-21.
CrossRef - International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetic Atlas 7th Edition. http://www.idf.org/idf-diabetes-atlas-seventh-edition.
- Morales M.C, Navas A.F and Jimenez M.F.R. Health- related quality of life in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in a rural area. J. Diabetes Metab. 2015;6:1-5.
- Tripathy J and Thakur J. S. Prevalence and risk factors of diabetes in a large community-based study in north India: results from a STEPS survey in Punjab, India. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2017;9:1-8.
CrossRef - Kapur A. Influence of socio-economic factors on diabetes care. Int. J. Diab Dev Countries. 2001;21:77-85.
- Australian institute of health and welfare, Diabetes: Australian facts .Diabetes series No. 8. Cat. no. CVD 40. Canberra: AIHW. 2008.
- Mustapha W, Hossain Z,S and Loughlin K. O. Management and impact of diabetes on quality of life among the Lebanese community of Sydney: A quantitative study. J. Diabetes Metab. 2014;5:1-10.
CrossRef - Stanetic K, Savic S and Racic M. The quality of life of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. 2012;18:70-77.
- Thommasen H.V and Zhang W. Impact of chronic disease on quality of life in the Bella Coola Valley. Rural remote health. 2006;6:528.
- Crouchley K.D and Chronic disease and quality of life in western Australia. Department of health, western Australia. 2007:5–8.
- Aghamollaei T and Eftekhar H. Behavior, metabolic control and health-related quality of life in diabetic patients at Bandar Abbas diabetic clinic. Iranian. J. Publ Health. 2003;32:54–59.
- Caro J.J, Ward A.J and Brien J.A. Lifetime costs of complications resulting from type 2 diabetes in the U.S. Diabetes Care. 2002;25:476–481.
CrossRef - Nichols G.A, Arondekar B and Herman W.h. Medical care costs one year after identification of hyperglycemia below the threshold for diabetes. Med Care. 2008;46:287–292.
CrossRef - Piette J.D, Heisler M and Wagner T.H. Problems paying out-of-pocket medication costs among older adults with diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2004;27:384–391.
CrossRef - Piette J.D, Wagner T.H, Potter M.B and Schillinger D. Health insurance status, cost related medication underuse, and outcomes among diabetes patients in three systems of care. Med Care. 2004;42:102–109.
CrossRef - Bodenheimer T, Wagner E.H and Grumbach K. Improving primary care for patients with chronic illness: the chronic care model, Part 2. J. Am Med Assoc. 2002;288:1909–1914.
CrossRef - Tuomilehto J, Lindstrom J, Eriksson J.G and Prevention of type 2 diabetes mellitus by changes in lifestyle among subjects with impaired glucose tolerance. N Engl. J. Med. 2001;344:1343-1350.
CrossRef - Ware J.E and Sherbourne C.D. The MOS 36-item short-form health survey (SF-36). Conceptual frame work and item selection. Med Care. 1992;30:473-483.
CrossRef - Carey MO. RCMAR measurement tools, Appraisal of diabetes scale. http://www.musc.edu/dfm/RCMAR/ADS.html. 2006.
- Sevick M.A, Dunn A.L, Morrow M.S, Marcus B.H, Chen G.J and Blair S.N. Cost effectiveness of lifestyle and structured exercise intervention in sedentary adults: Results of project ACTIVE. Am. J. Prev Med. 2000:19:1-8.
CrossRef - Upadhyay D. K, Ibrahim M, Mishra P and Vijay M. Does pharmacist supervised intervention through pharmaceutical care program influence direct healthcare cost burden of newly diagnosed diabetics in a tertiary care teaching hospital in Nepal: A non-clinical randomized controlled trial approach DARU. Pharm. Sci. 2016;24:1-9.
CrossRef - Odnoletkova I, Ramaekers D, Nobels F, Goderis G, Aertgeerts B and Annemans L. Delivering diabetes education through nurse-led telecoaching. cost-effectiveness analysis. PLoS One. 2016;11:(16):39-97.
CrossRef - Anne M and Wolf MS R.D. Effects of lifestyle intervention on health care costs: improving control with activity and nutrition (ICAN). J. Am Diet Assoc. 2007;107:1365-1373.
CrossRef - Wolf A.M, Conaway M.R and Crowther J.Q. Translating lifestyle intervention to practice in obese patients with type 2 diabetes: Improving control with activity and nutrition (ICAN). Diabetes Care. 2004;27:1570-1576.
CrossRef - Png M.E and Yoong J.S-Y. Evaluating the cost-effectiveness of lifestyle modification versus metformin therapy for the prevention of diabetes in Singapore. doi:10.1371. journal Plos One.pone. 2014;9:107225-107225
- Lin E.H, Katon W and Rutter C. Effects of enhanced depression treatment on diabetes self-care. Ann Fam Med. 06;4:46-53.
CrossRef - Ibrahim N, Ming Moy F and Awalludin IAN. Effects of a community-based healthy lifestyle intervention program (co-help) among adults with pre-diabetes in a developing country: a quasi-experimental study. PLoS One. 2016;11:167-123.
CrossRef - Rajeshwari S. Adhikari Prabha MR and Pai MRSM. Drug utilization study in geriatric Type 2 diabetic patients. J. Clin Diagn Res. 2009;5:440-443.
- Kaskurthy S Nalluri H. L and Thanait D. R. Influence of education on quality of life in type 2 diabetic patients in a tertiary care teaching hospital. World. J. Pharm Pharm Sci. 2014;3(11):1344-1353.
- Testa M.A, Simonson D.C and Turner R.R. Valuing quality of life and improvement in glycemic control in people with type-2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 1998;21:44-52.
CrossRef - Shareef J, Fernandes J and Samaga L. Impact of pharmacist’s intervention on improving quality of life in patients with diabetes mellitus. J. Diabetes Metab Disord Control. 2016;3:00076. DOI: 10.15406/jdmdc. 2016;3:76
CrossRef - Sriram S, Damodharan S and Akhila S. A. Impact of pharmaceutical care activities on diabetic patients at a private corporate hospital. 2016;5:66-74.
- Amjad R. N, Rasouli D and Mohammadpour Y. Comparison of effectiveness of self-empowerment through educational package and workshop in quality of life of diabetic patients. Jundishapur. Chronic. Dis. Care. 2016;5:37186.
- Adepu R, Rasheed A and Nagavi B.G. Effect of patient counseling on quality of life in Type‐2 diabetes mellitus patients in two selected south Indian community pharmacies : A study. Indian. J. Pharm. Sci. 2007;69:519‐5
CrossRef - Carvalho S and Nagavi B.G. Impact of community pharmacy based patient education on the quality of life of hypertensive patients. Indian. J. Pharm Edu Res. 2007;41:1-164
- Jahromi M K, Somayeh Ramezanl S and Taheri L. Effectiveness of diabetes self-management education on quality of life in diabetic elderly females. Glob. J. Health Sci. 2015;7(1):10-15.
- Didarloo A, Shojaeizadeh D and Alizadeh M. Impact of educational intervention based on interactive approaches on beliefs, behavior, hemoglobin A1c, and quality of life in diabetic women. Int. J. Prev Med. 2016;7: 1-8.
- Jacobsen R, VadstrupE and Roder M. Predictors of effects of lifestyle intervention on diabetes mellitus type 2 patients. World. J. Article ID. 2012;96(2951);1- 8.
- Maxwell O, Adibe and Chinwe V. The impact of pharmaceutical care intervention on the quality of life of nigerian patients receiving treatment for type 2 diabetes. Value Health Reg Issues. 2013;2 :240-247
CrossRef







